Rosuvastatin Improves Vaspin Serum Levels in Obese Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome
- PMID: 29337850
- PMCID: PMC5871955
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases6010009
Rosuvastatin Improves Vaspin Serum Levels in Obese Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome
Abstract
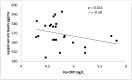
Adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor (vaspin), which has endocrine and local roles in atherosclerosis growth, is also synthesized by adipose tissue; it was found that vaspin was negatively correlated with blood pressure in obese patients, while vaspin levels were decreased in endothelial dysfunction. The aim of the present study was to determine rosuvastatin modulation effects on serum vaspin levels in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) with class I obesity. A total number of seventy patients with acute coronary syndrome previously and currently treated with rosuvastatin was compared to 40 patients with IHD not treated by rosuvastatin as a control. Vaspin serum levels were higher in rosuvastatin-treated patients with acute coronary syndrome compared to the patients with acute coronary syndrome not treated by rosuvastatin, p < 0.01. Additionally, in the rosuvastatin-treated group, patients with STEMI showed higher vaspin serum levels compared to NSTEMI p < 0.01.
Conclusion: Rosuvastatin significantly increases vaspin serum levels in acute coronary syndrome.
Keywords: NSTEMI; STEMI; acute coronary syndrome; vaspin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Tsaousi G., Pitsis A.A., Ioannidis G.D., Vasilakos D.G. A multidisciplinary approach to unplanned conversion from off-pump to on-pump beating heart coronary artery revascularization in patients with compromised left ventricular function. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2014;2014:348021. doi: 10.1155/2014/348021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Erne P., Radovanovic D., Seifert B., Bertel O., Urban P., AMIS Plus Investigators The outcome of patients admitted with acute coronary syndrome on palliative treatment: Insights from the nationwide AMIS Plus Registry 1997–2014. BMJ Open. 2015;5:e006218. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006218. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hicks K., Cocks K., Corbacho Martin B., Elton P., MacNab A., Colecliffe W., Furze G. An intervention to reassure patients about test results in rapid access chest pain clinic: A pilot randomised controlled trial. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2014;14:138. doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-14-138. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

