Monitoring Strategies of Earth Dams by Ground-Based Radar Interferometry: How to Extract Useful Information for Seismic Risk Assessment
- PMID: 29337884
- PMCID: PMC5795412
- DOI: 10.3390/s18010244
Monitoring Strategies of Earth Dams by Ground-Based Radar Interferometry: How to Extract Useful Information for Seismic Risk Assessment
Abstract
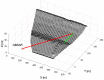
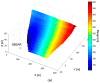
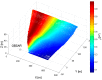
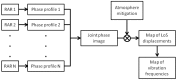
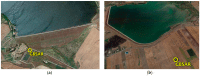
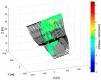
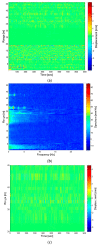
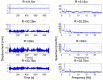
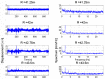
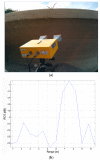
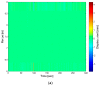
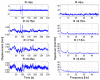
The aim of this paper is to describe how ground-based radar interferometry can provide displacement measurements of earth dam surfaces and of vibration frequencies of its main concrete infrastructures. In many cases, dams were built many decades ago and, at that time, were not equipped with in situ sensors embedded in the structure when they were built. Earth dams have scattering properties similar to landslides for which the Ground-Based Synthetic Aperture Radar (GBSAR) technique has been so far extensively applied to study ground displacements. In this work, SAR and Real Aperture Radar (RAR) configurations are used for the measurement of earth dam surface displacements and vibration frequencies of concrete structures, respectively. A methodology for the acquisition of SAR data and the rendering of results is described. The geometrical correction factor, needed to transform the Line-of-Sight (LoS) displacement measurements of GBSAR into an estimate of the horizontal displacement vector of the dam surface, is derived. Furthermore, a methodology for the acquisition of RAR data and the representation of displacement temporal profiles and vibration frequency spectra of dam concrete structures is presented. For this study a Ku-band ground-based radar, equipped with horn antennas having different radiation patterns, has been used. Four case studies, using different radar acquisition strategies specifically developed for the monitoring of earth dams, are examined. The results of this work show the information that a Ku-band ground-based radar can provide to structural engineers for a non-destructive seismic assessment of earth dams.
Keywords: Real Aperture Radar (RAR); SAR interferometry; Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR); earth dam; ground-based radar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



















References
-
- Massonnet D., Feigl K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998;36:441–500. doi: 10.1029/97RG03139. - DOI
-
- Prats P., Reigber A., Mallorqui J.J., Scheiber R., Moreira A. Estimation of the temporal evolution of the deformation using airborne differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008;46:1065–1078. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.915758. - DOI
-
- Montserrat O., Crosetto M., Luzi G. A review of ground-based SAR interferometry for deformation measurement. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014;93:40–48. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.04.001. - DOI
-
- Oliveira S.C., Zezêre J.L., Catalão J., Nico G. The contribution of PSInSAR interferometry to landslide hazard in weak rock-dominated areas. Landslides. 2015;12:703–719. doi: 10.1007/s10346-014-0522-9. - DOI
-
- Leva D., Nico G., Tarchi D., Fortuny-Guasch J., Sieber A.J. Temporal analysis of a landslide by means of a ground-based SAR interferometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003;41:745–752. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.808902. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

