Distribution of cone density, spacing and arrangement in adult healthy retinas with adaptive optics flood illumination
- PMID: 29338027
- PMCID: PMC5770065
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191141
Distribution of cone density, spacing and arrangement in adult healthy retinas with adaptive optics flood illumination
Abstract
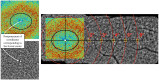
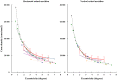
The aim of this article is to analyse cone density, spacing and arrangement using an adaptive optics flood illumination retina camera (rtx1™) on a healthy population. Cone density, cone spacing and packing arrangements were measured on the right retinas of 109 subjects at 2°, 3°, 4°, 5° and 6° of eccentricity along 4 meridians. The effects of eccentricity, meridian, axial length, spherical equivalent, gender and age were evaluated. Cone density decreased on average from 28 884 ± 3 692 cones/mm2, at 2° of eccentricity, to 15 843 ± 1 598 cones/mm2 at 6°. A strong inter-individual variation, especially at 2°, was observed. No important difference of cone density was observed between the nasal and temporal meridians or between the superior and inferior meridians. However, the horizontal and vertical meridians differed by around 14% (T-test, p<0.0001). Cone density, expressed in units of area, decreased as a function of axial length (r2 = 0.60), but remained constant (r2 = 0.05) when cone density is expressed in terms of visual angle supporting the hypothesis that the retina is stretched during the elongation of the eyeball. Gender did not modify the cone distribution. Cone density was slightly modified by age but only at 2°. The older group showed a smaller density (7%). Cone spacing increased from 6,49 ± 0,42 μm to 8,72 ± 0,45 μm respectively between 2° and 6° of eccentricity. The mosaic of the retina is mainly triangularly arranged (i.e. cells with 5 to 7 neighbors) from 2° to 6°. Around half of the cells had 6 neighbors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Osterberg G. Topography of the layer of rods and cones in the human retina. Acta ophthal Suppl. 1935;6:11–97.
-
- Curcio CA, Sloan KR, Kalina RE, Hendrickson AE. Human photoreceptor topography. J Comp Neurol. 1990;292(4):497–523. doi: 10.1002/cne.902920402 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li KY, Roorda A. Automated identification of cone photoreceptors in adaptive optics retinal images. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2007;24(5):1358–63. . - PubMed
-
- Chui TY, Song H, Burns SA. Individual variations in human cone photoreceptor packing density: variations with refractive error. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008;49(10):4679–87. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2135 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

