A live cell assay of GPCR coupling allows identification of optogenetic tools for controlling Go and Gi signaling
- PMID: 29338718
- PMCID: PMC5771134
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-017-0475-2
A live cell assay of GPCR coupling allows identification of optogenetic tools for controlling Go and Gi signaling
Abstract
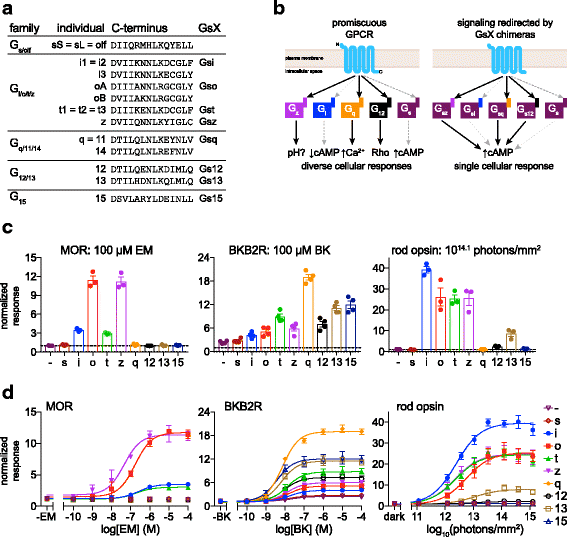
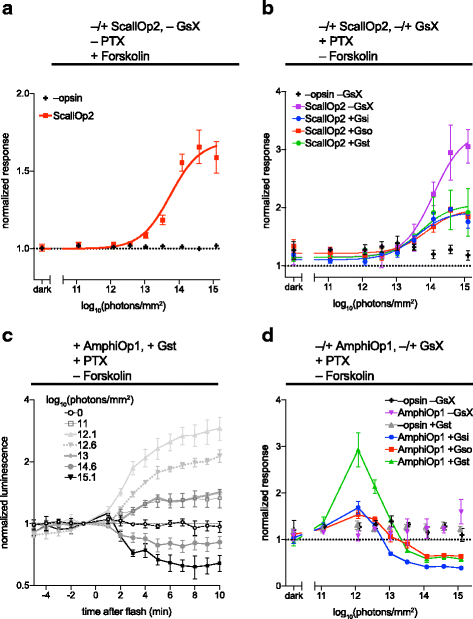
Background: Animal opsins are light-sensitive G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that enable optogenetic control over the major heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathways in animal cells. As such, opsins have potential applications in both biomedical research and therapy. Selecting the opsin with the best balance of activity and selectivity for a given application requires knowing their ability to couple to a full range of relevant Gα subunits. We present the GsX assay, a set of tools based on chimeric Gs subunits that transduce coupling of opsins to diverse G proteins into increases in cAMP levels, measured with a real-time reporter in living cells. We use this assay to compare coupling to Gi/o/t across a panel of natural and chimeric opsins selected for potential application in gene therapy for retinal degeneration.
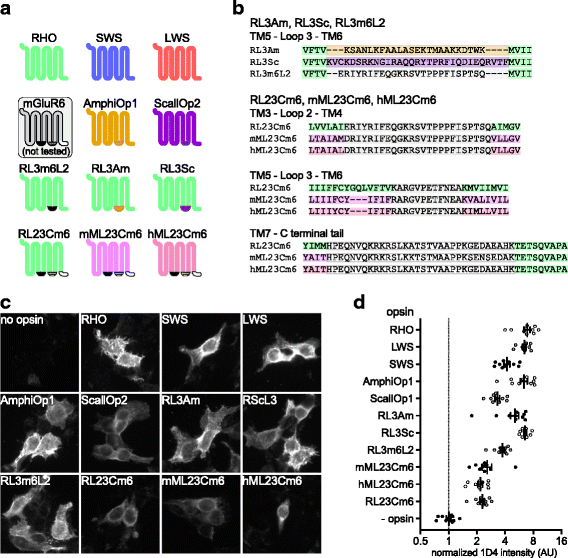
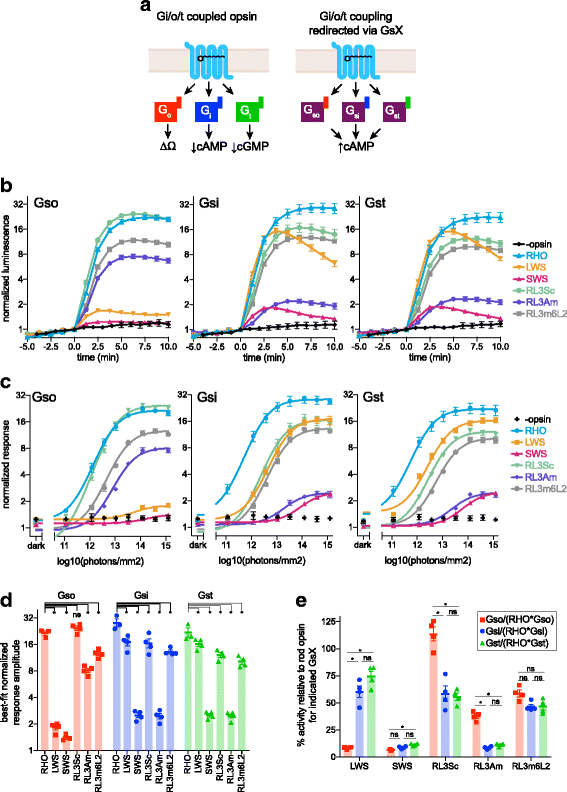
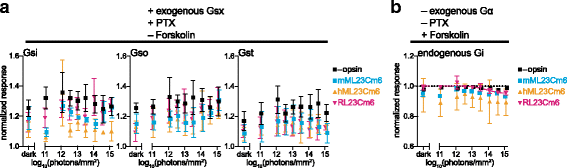
Results: Of the opsins tested, wild-type human rod opsin had the highest activity for chimeric Gs proxies for Gi and Gt (Gsi and Gst) and was matched in Go proxy (Gso) activity only by a human rod opsin/scallop opsin chimera. Rod opsin drove roughly equivalent responses via Gsi, Gso, and Gst, while cone opsins showed much lower activities with Gso than Gsi or Gst, and a human rod opsin/amphioxus opsin chimera demonstrated higher activity with Gso than with Gsi or Gst. We failed to detect activity for opsin chimeras bearing three intracellular fragments of mGluR6, and observed unexpectedly complex response profiles for scallop and amphioxus opsins thought to be specialized for Go.
Conclusions: These results identify rod opsin as the most potent non-selective Gi/o/t-coupled opsin, long-wave sensitive cone opsin as the best for selectively activating Gi/t over Go, and a rod opsin/amphioxus opsin chimera as the best choice for selectively activating Go over Gi/t.
Keywords: Cell signaling; GPCR; GalphaO; Gene therapy; Opsin; Optogenetics; Retinal degeneration; Synthetic biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
RJL is a named inventor on a patent application for the use of rod opsin as a therapeutic in retinal degeneration that is currently licensed for clinical development by Acucela Inc. and he has previously provided consultancy services to them on this topic.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

