A Novel Inhibitor of the LolCDE ABC Transporter Essential for Lipoprotein Trafficking in Gram-Negative Bacteria
- PMID: 29339384
- PMCID: PMC5913989
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02151-17
A Novel Inhibitor of the LolCDE ABC Transporter Essential for Lipoprotein Trafficking in Gram-Negative Bacteria
Abstract
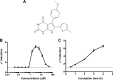
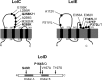
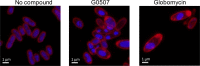
The outer membrane is an essential structural component of Gram-negative bacteria that is composed of lipoproteins, lipopolysaccharides, phospholipids, and integral β-barrel membrane proteins. A dedicated machinery, called the Lol system, ensures proper trafficking of lipoproteins from the inner to the outer membrane. The LolCDE ABC transporter is the inner membrane component, which is essential for bacterial viability. Here, we report a novel pyrrolopyrimidinedione compound, G0507, which was identified in a phenotypic screen for inhibitors of Escherichia coli growth followed by selection of compounds that induced the extracytoplasmic σE stress response. Mutations in lolC, lolD, and lolE conferred resistance to G0507, suggesting LolCDE as its molecular target. Treatment of E. coli cells with G0507 resulted in accumulation of fully processed Lpp, an outer membrane lipoprotein, in the inner membrane. Using purified protein complexes, we found that G0507 binds to LolCDE and stimulates its ATPase activity. G0507 still binds to LolCDE harboring a Q258K substitution in LolC (LolCQ258K), which confers high-level resistance to G0507 in vivo but no longer stimulates ATPase activity. Our work demonstrates that G0507 has significant promise as a chemical probe to dissect lipoprotein trafficking in Gram-negative bacteria.
Keywords: LolCDE; antibiotic discovery; lipoprotein trafficking; outer membrane biogenesis; phenotypic assay; stress response.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



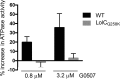

Similar articles
-
Genetic analysis reveals a robust and hierarchical recruitment of the LolA chaperone to the LolCDE lipoprotein transporter.mBio. 2024 Feb 14;15(2):e0303923. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03039-23. Epub 2024 Jan 9. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38193657 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule inhibitors of gram-negative lipoprotein trafficking discovered by phenotypic screening.J Bacteriol. 2015 Mar;197(6):1075-82. doi: 10.1128/JB.02352-14. Epub 2015 Jan 12. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25583975 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of the mode of interplay between an ATPase subunit and membrane subunits of the lipoprotein-releasing ATP-binding cassette transporter LolCDE.J Bacteriol. 2006 Apr;188(8):2856-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.8.2856-2864.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16585747 Free PMC article.
-
Sorting of lipoproteins to the outer membrane in E. coli.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Nov 11;1694(1-3):IN1-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15672528 Review.
-
ABC transporters involved in the biogenesis of the outer membrane in gram-negative bacteria.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75(6):1044-54. doi: 10.1271/bbb.110115. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21670534 Review.
Cited by
-
Making a chink in their armor: Current and next-generation antimicrobial strategies against the bacterial cell envelope.Adv Microb Physiol. 2023;83:221-307. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2023.05.003. Epub 2023 Jun 27. Adv Microb Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37507160 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of a previously uncharacterized lipoprotein lirL confers resistance to an inhibitor of type II signal peptidase in Acinetobacter baumannii.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Sep 20;119(38):e2123117119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2123117119. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36099298 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical genetic approaches for the discovery of bacterial cell wall inhibitors.RSC Med Chem. 2023 Aug 30;14(11):2125-2154. doi: 10.1039/d3md00143a. eCollection 2023 Nov 15. RSC Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37974958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New strategies and structural considerations in development of therapeutics for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae.Transl Res. 2020 Jun;220:14-32. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2020.02.008. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32201344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Causal association between gastroesophageal reflux disease and sepsis, and the mediating role of gut bacterial abundance, a Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Feb 21;104(8):e41631. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041631. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39993106 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

