Chronic dietary creatine enhances hippocampal-dependent spatial memory, bioenergetics, and levels of plasticity-related proteins associated with NF-κB
- PMID: 29339557
- PMCID: PMC5772392
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.046284.117
Chronic dietary creatine enhances hippocampal-dependent spatial memory, bioenergetics, and levels of plasticity-related proteins associated with NF-κB
Abstract
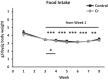
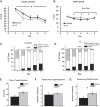
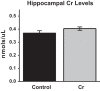
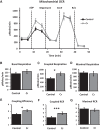
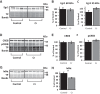
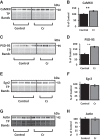
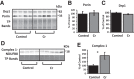
The brain has a high demand for energy, of which creatine (Cr) is an important regulator. Studies document neurocognitive benefits of oral Cr in mammals, yet little is known regarding their physiological basis. This study investigated the effects of Cr supplementation (3%, w/w) on hippocampal function in male C57BL/6 mice, including spatial learning and memory in the Morris water maze and oxygen consumption rates from isolated mitochondria in real time. Levels of transcription factors and related proteins (CREB, Egr1, and IκB to indicate NF-κB activity), proteins implicated in cognition (CaMKII, PSD-95, and Egr2), and mitochondrial proteins (electron transport chain Complex I, mitochondrial fission protein Drp1) were probed with Western blotting. Dietary Cr decreased escape latency/time to locate the platform (P < 0.05) and increased the time spent in the target quadrant (P < 0.01) in the Morris water maze. This was accompanied by increased coupled respiration (P < 0.05) in isolated hippocampal mitochondria. Protein levels of CaMKII, PSD-95, and Complex 1 were increased in Cr-fed mice, whereas IκB was decreased. These data demonstrate that dietary supplementation with Cr can improve learning, memory, and mitochondrial function and have important implications for the treatment of diseases affecting memory and energy homeostasis.
© 2018 Snow et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

References
-
- Aksenov MY, Aksenova MV, Carney JM, Butterfield DA. 1997. Oxidative modification of glutamine synthetase by amyloid β peptide. Free Radic Res 27: 267–281. - PubMed
-
- Allahyar R, Akbar A, Iqbal F. 2015. Creatine monohydrate supplementation for 10 weeks mediates neuroprotection and improves learning/memory following neonatal hypoxia ischemia encephalopathy in female albino mice. Brain Res 1595: 92–100. - PubMed
-
- Allahyar R, Akbar A, Iqbal F. 2016. Effect of creatine monohydrate supplementation on learning, memory and neuromuscular coordination in female albino mice. Acta Neuropsychiatr 29: 27–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
