The deep-subsurface sulfate reducer Desulfotomaculum kuznetsovii employs two methanol-degrading pathways
- PMID: 29339722
- PMCID: PMC5770442
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-02518-9
The deep-subsurface sulfate reducer Desulfotomaculum kuznetsovii employs two methanol-degrading pathways
Abstract
Methanol is generally metabolized through a pathway initiated by a cobalamine-containing methanol methyltransferase by anaerobic methylotrophs (such as methanogens and acetogens), or through oxidation to formaldehyde using a methanol dehydrogenase by aerobes. Methanol is an important substrate in deep-subsurface environments, where thermophilic sulfate-reducing bacteria of the genus Desulfotomaculum have key roles. Here, we study the methanol metabolism of Desulfotomaculum kuznetsovii strain 17T, isolated from a 3000-m deep geothermal water reservoir. We use proteomics to analyze cells grown with methanol and sulfate in the presence and absence of cobalt and vitamin B12. The results indicate the presence of two methanol-degrading pathways in D. kuznetsovii, a cobalt-dependent methanol methyltransferase and a cobalt-independent methanol dehydrogenase, which is further confirmed by stable isotope fractionation. This is the first report of a microorganism utilizing two distinct methanol conversion pathways. We hypothesize that this gives D. kuznetsovii a competitive advantage in its natural environment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
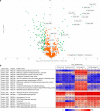
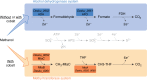



References
-
- Gniese C, et al. Relevance of deep-subsurface microbiology for underground gas storage and geothermal energy production. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2014;142:95–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

