TGR5 signalling promotes mitochondrial fission and beige remodelling of white adipose tissue
- PMID: 29339725
- PMCID: PMC5770450
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-02068-0
TGR5 signalling promotes mitochondrial fission and beige remodelling of white adipose tissue
Abstract
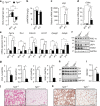
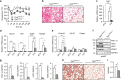
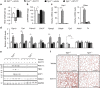
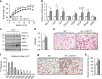
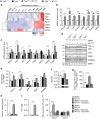
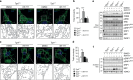
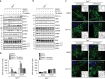
Remodelling of energy storing white fat into energy expending beige fat could be a promising strategy to reduce adiposity. Here, we show that the bile acid-responsive membrane receptor TGR5 mediates beiging of the subcutaneous white adipose tissue (scWAT) under multiple environmental cues including cold exposure and prolonged high-fat diet feeding. Moreover, administration of TGR5-selective bile acid mimetics to thermoneutral housed mice leads to the appearance of beige adipocyte markers and increases mitochondrial content in the scWAT of Tgr5 +/+ mice but not in their Tgr5 -/- littermates. This phenotype is recapitulated in vitro in differentiated adipocytes, in which TGR5 activation increases free fatty acid availability through lipolysis, hence fuelling β-oxidation and thermogenic activity. TGR5 signalling also induces mitochondrial fission through the ERK/DRP1 pathway, further improving mitochondrial respiration. Taken together, these data identify TGR5 as a druggable target to promote beiging with potential applications in the management of metabolic disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Adipose tissue: Bile acid-TGR5 axis promotes beiging.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018 Mar;14(3):130. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2018.13. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29393300 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

