Anti-apoptotic A1 is not essential for lymphoma development in Eµ-Myc mice but helps sustain transplanted Eµ-Myc tumour cells
- PMID: 29339775
- PMCID: PMC5864240
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-017-0045-8
Anti-apoptotic A1 is not essential for lymphoma development in Eµ-Myc mice but helps sustain transplanted Eµ-Myc tumour cells
Abstract
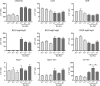
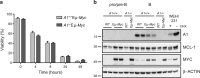
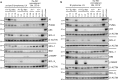
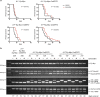
The transcription factor c-MYC regulates a multiplicity of genes involved in cellular growth, proliferation, metabolism and DNA damage response and its overexpression is a hallmark of many tumours. Since MYC promotes apoptosis under conditions of stress, such as limited availability of nutrients or cytokines, MYC-driven cells are very much dependent on signals that inhibit cell death. Stress signals trigger apoptosis via the pathway regulated by opposing fractions of the BCL-2 protein family and previous genetic studies have shown that the development of B lymphoid tumours in Eµ-Myc mice is critically dependent on expression of pro-survival BCL-2 relatives MCL-1, BCL-W and, to a lesser extent, BCL-XL, but not BCL-2 itself, and that sustained growth of these lymphomas is dependent on MCL-1. Using recently developed mice that lack expression of all three functional pro-survival A1 genes, we show here that the kinetics of lymphoma development in Eµ-Myc mice and the competitive repopulation capacity of Eµ-Myc haemopoietic stem and progenitor cells is unaffected by the absence of A1. However, conditional loss of a single remaining functional A1 gene from transplanted A1-a-/-A1-b fl/fl A1-c-/- Eµ-Myc lymphomas slowed their expansion, significantly extending the life of the transplant recipients. Thus, A1 contributes to the survival of malignant Eµ-Myc-driven B lymphoid cells. These results strengthen the case for BFL-1, the human homologue of A1, being a valid target for drug development for MYC-driven tumours.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Askew DS, Ashmun RA, Simmons BC, Cleveland JL. Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene. 1991;6:1915–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

