Bilateral Radiation Optic Neuropathy Following Concurrent Chemotherapy and Radiation in Glioblastoma
- PMID: 29339965
- PMCID: PMC5762177
- DOI: 10.1080/01658107.2017.1322989
Bilateral Radiation Optic Neuropathy Following Concurrent Chemotherapy and Radiation in Glioblastoma
Abstract
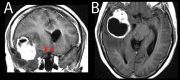
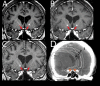
Radiation optic neuropathy (RON) is an iatrogenic complication that causes severe, irreversible vision loss within months to years following radiation to lesions close to the visual pathway. The authors describe a case of RON in glioblastoma after radio-sensitisation with temozolomide with sequential involvement of both optic nerves. This case provides a timeline for clinical and imaging findings with RON and specifically resolution of nerve enhancement. The authors also highlight the potential of an increase in incidence of RON in glioblastoma with advances in survival seen with greater use of second-line chemotherapy and even re-radiation.
Keywords: Glioblastoma; radiation optic neuropathy; temozolomide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optic nerve and visual pathways primary glioblastoma treated with radiotherapy and temozolomide chemotherapy.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2014 Jul-Aug;24(4):637-40. doi: 10.5301/ejo.5000416. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24366773
-
Radiation-induced optic neuropathy.J Clin Neurosci. 2008 Feb;15(2):95-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2007.09.004. J Clin Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18068989 Review.
-
In search of a treatment for radiation-induced optic neuropathy.Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2015 Jan;17(1):325. doi: 10.1007/s11940-014-0325-2. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25398466
-
Optic neuropathy following orbital irradiation for Graves' ophthalmopathy: a case report and literature review.Orbit. 2012 Feb;31(1):30-3. doi: 10.3109/01676830.2011.603458. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Orbit. 2012. PMID: 22029640 Review.
-
Radiation optic neuropathy and retinopathy with low dose (20 Gy) radiation treatment.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2016 Jun 29;3:50-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2016.06.008. eCollection 2016 Oct. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 29503909 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects and Assessment of the Optic Pathway After Management with Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Intracranial Tumors: A Comprehensive Literature Review.Cureus. 2023 Aug 15;15(8):e43538. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43538. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37719564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of safety and efficacy of proton radiotherapy for optic nerve sheath meningioma.Neurooncol Adv. 2024 Sep 21;6(1):vdae160. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdae160. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Neurooncol Adv. 2024. PMID: 39434923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lessell S. Friendly fire: neurogenic visual loss from radiation therapy. J Neuro-ophthalmol 2004;24:243–250. - PubMed
-
- Roden D, Bosley TM, Fowble B, Clark J, Savino PJ, Sergott RC, Schatz NJ.. Delayed radiation injury to the retrobulbar optic nerves and chiasm. Clinical syndrome and treatment with hyperbaric oxygen and corticosteroids. Ophthalmology 1990;97:346–351. - PubMed
-
- Kline LB, Kim JY, Ceballos R.. Radiation optic neuropathy. Ophthalmology 1985;92:1118–1126. - PubMed
-
- Demizu Y, Murakami M, Miyawaki D, Niwa Y, Akagi T, Sasaki R, Terashima K, Suga D, Kamae I, Hishikawa Y.. Analysis of Vision loss caused by radiation-induced optic neuropathy after particle therapy for head-and-neck and skull-base tumors adjacent to optic nerves. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;75:1487–1492. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
