Multidisciplinary treatment of patients with diabetes and hypertension: experience of a Brazilian center
- PMID: 29339974
- PMCID: PMC5759874
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-017-0305-2
Multidisciplinary treatment of patients with diabetes and hypertension: experience of a Brazilian center
Abstract
Background: Although multidisciplinary treatment is recommended for type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension (HTN), there is a lack of scientific literature supporting the hypothesis of extending this treatment strategy to patients with both diabetes and HTN. Aiming to report results of long-term multidisciplinary treatment for these patients and identify strategies to improve their management, we conducted this study.
Methods: Data of patients with diabetes and HTN with regular follow-up visits in a multidisciplinary HTN treatment center from Brazil's Midwest were retrospectively assessed. Patients ≥ 18 years enrolled in the service by June 2017 with a minimum of three visits were included. Anthropometric, blood pressure (BP), laboratory, pharmacological treatment, lifestyle, and cardiovascular events data were collected from first (V1), intermediate (V2) and most recent (V3) visits to the service. BP < 130 × 80 mmHg, LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) < 70 mg/dL and HbA1C < 7.0% were defined as treatment targets. Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare variables along study visits. A linear regression model was built to identify variables associated with better overall patient control.
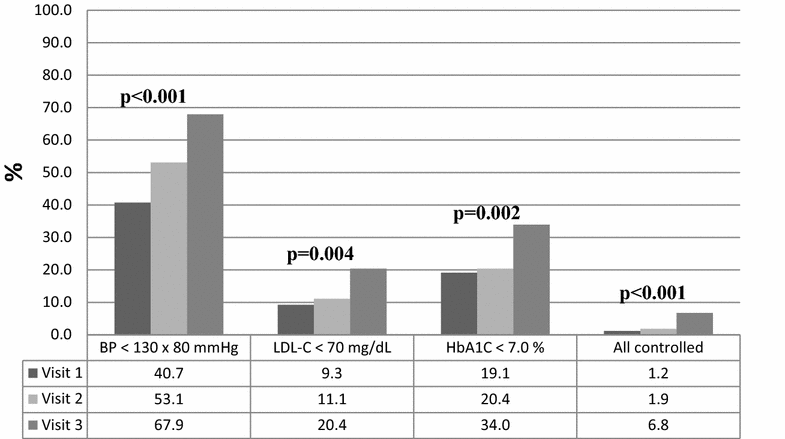
Results: A total of 162 patients were included (mean age of 56.5 ± 10.8 years). Median follow-up time was 60 (IQR 40-109) months, 80.2% of the sample was female and 83.3% had no cardiovascular event history. BP, total cholesterol, LDL-C, triglycerides and HbA1C values showed a significant trend to improve along the study visits (p < 0.001). Growing trend in aspirin (p = 0.045) and statins (p < 0.001) use was found, in addition to treatment compliance increase (p < 0.001). Significant improvement trends in BP (p < 0.001), LDL-C (p = 0.004) and HbA1C (p = 0.002) control were also found across visits. Control rates of BP, LDL-C and HbA1C in combination were low in V1, V2 and V3 (1.2, 1.9 and 6.8%, respectively), but showed significant improvement trend (p < 0.001). Treatment compliance (β-coefficient = 1.20; 95% CI 1.07-1.34; p < 0.001) was positively associated with better overall patients control.
Conclusions: Multidisciplinary treatment of patients with diabetes and HTN significantly improved clinical and laboratory parameters, despite ageing of population evaluated. Although combined control of HbA1C, BP and LDL-cholesterol increased along follow-up, management of all these three conditions needs to improve, and focus on treatment compliance should be given to attain this goal.
Keywords: Diabetes; Hypertension; Multidisciplinary treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Turner RC, Holman RR, Matthews DR, Bassett PA, Coster R, Stratton IM, Cull C, Peto R, Frighi V, Kennedy I, Manley S. Hypertension in Diabetes Study (HDS): I. Prevalence of hypertension in newly presenting type 2 diabetic patients and the association with risk factors for cardiovascular and diabetic complications. J Hypertens. 1993;11(3):309–317. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199303000-00012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chew BH, Mastura I, Shariff-Ghazali S, Lee PY, Cheong AT, Ahmad Z, Taher SW, Haniff J, Mustapha FI, Bujang MA. Determinants of uncontrolled hypertension in adult type 2 diabetes mellitus: an analysis of the Malaysian diabetes registry 2009. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012;11(1):54. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-11-54. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources