Functional and Muscle-Size Effects of Flywheel Resistance Training with Eccentric-Overload in Professional Handball Players
- PMID: 29339993
- PMCID: PMC5765793
- DOI: 10.1515/hukin-2017-0096
Functional and Muscle-Size Effects of Flywheel Resistance Training with Eccentric-Overload in Professional Handball Players
Abstract
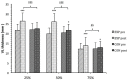
The aim of the study was to analyse the effects of 6 week (15 sessions) flywheel resistance training with eccentric-overload (FRTEO) on different functional and anatomical variables in professional handball players. Twenty-nine athletes were recruited and randomly divided into two groups. The experimental group (EXP, n = 15) carried out 15 sessions of FRTEO in the leg-press exercise, with 4 sets of 7 repetitions at a maximum-concentric effort. The control group (CON, n = 14) performed the same number of training sessions including 4 sets of 7 maximum repetitions (7RM) using a weight-stack leg-press machine. The results which were measured included maximal dynamic strength (1RM), muscle power at different submaximal loads (PO), vertical jump height (CMJ and SJ), 20 m sprint time (20 m), T-test time (T-test), and Vastus-Lateralis muscle (VL) thickness. The results of the EXP group showed a substantially better improvement (p < 0.05-0.001) in PO, CMJ, 20 m, T-test and VL, compared to the CON group. Moreover, athletes from the EXP group showed significant improvements concerning all the variables measured: 1RM (ES = 0.72), PO (ES = 0.42 - 0.83), CMJ (ES = 0.61), SJ (ES = 0.54), 20 m (ES = 1.45), T-test (ES = 1.44), and VL (ES = 0.63 - 1.64). Since handball requires repeated short, explosive effort such as accelerations and decelerations during sprints with changes of direction, these results suggest that FRTEO affects functional and anatomical changes in a way which improves performance in well-trained professional handball players.
Keywords: hypertrophy; iso-inertial; muscle power; sport performance.
Figures

References
-
- Alegre LM, Aguado X, Rojas-Martin D, Martin-Garcia M, Ara I, Csapo R.. Load-controlled moderate and high-intensity resistance training programs provoke similar strength gains in young women. Muscle Nerve. 2015;51(1):92–101. - PubMed
-
- Alegre LM, Ferri-Morales A, Rodriguez-Casares R, Aguado X.. Effects of isometric training on the knee extensor moment-angle relationship and vastus lateralis muscle architecture. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2014;114(11):2437–2446. - PubMed
-
- Alkner B, Tesch PA.. Efficacy of a gravity-independent resistance exercise device as a countermeasure to muscle atrophy during 29-day bed rest. Acta Physiol Scand. 2004;181:345–357. - PubMed
-
- Alkner BA, Berg HE, Kozlovskaya I, Sayenko D, Tesch P.. Effects of strength training, using a gravity-independent exercise system, performed during 110 days of simulated space station confinement. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2003;90:44–49. - PubMed
-
- Askling C, Karlsson J, Thorstensson A.. Hamstring injury occurrence in elite soccer players after preseason strength training with eccentric overload. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2003;13(4):244–250. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
