Concurrent brain radiotherapy and EGFR-TKI may improve intracranial metastases control in non-small cell lung cancer and have survival benefit in patients with low DS-GPA score
- PMID: 29340055
- PMCID: PMC5762323
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.22785
Concurrent brain radiotherapy and EGFR-TKI may improve intracranial metastases control in non-small cell lung cancer and have survival benefit in patients with low DS-GPA score
Abstract
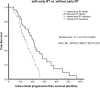
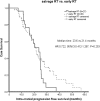
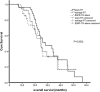
Epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) has intracranial activity in EGFR-mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). The optimal timing of brain radiotherapy (RT) and appropriate patients who need early brain RT remains undetermined. This is a retrospective study of EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases (BMs) before EGFR-TKI initiation. Intra-cranial progression free survival (IC-PFS) and overall survival (OS) were measured from the date of EGFR-TKI treatment. A total of 113 patients were eligible, 49 received concurrent early brain RT with EGFR-TKI and 64 were treated with EGFR-TKI alone as initial therapy, including 27 with salvage RT upon BM progression. The patients with early brain RT had superior IC-PFS than those without early brain RT (21.4 vs 15.0 months, P=0.001), which remained significant in multivariate analysis (HR 0.30, P<0.001). The median overall survival (OS) for early RT, EGFR-TKI alone and salvage RT groups was 28.1, 24.5, and 24.6 months, respectively (P=0.604). Similar IC-PFS (23.6 vs 21.4 months, P=0.253) and OS (24.6 vs 28.1 months, P=0.385) were observed between salvage RT and early RT groups. For patients with Diagnosis-Specific Graded Prognostic Assessment (DS-GPA) score of 0 to 2, early brain RT was the independent factor for improved OS (HR 0.33, P=0.025). In conclusion, concurrent early brain RT with EGFR-TKI may improve intracranial disease control in EGFR-mutant NSCLC with BM and have survival benefit in patients with low DS-GPA score. Salvage brain RT upon BM progression may be acceptable in some patients.
Keywords: EGFR mutation; EGFR-TKI; brain metastasis; brain radiotherapy; non-small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST All authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes according to initial and subsequent therapies following intracranial progression in patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancer and brain metastasis.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 16;15(4):e0231546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231546. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32298306 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Deferring Radiation Therapy in Patients With Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Who Develop Brain Metastases.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016 Jun 1;95(2):673-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.01.037. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016. PMID: 27034176
-
Analysis of the benefit of sequential cranial radiotherapy in patients with EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer and brain metastasis.Med Oncol. 2016 Aug;33(8):97. doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0811-3. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Med Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27447711 Free PMC article.
-
RT-based combination therapy for brain metastasis from NSCLC with non-EGFR mutation/ALK gene rearrangement: A network meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 28;12:1024833. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1024833. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36518310 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted drugs for systemic therapy of lung cancer with brain metastases.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 22;9(4):5459-5472. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23616. eCollection 2018 Jan 12. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29435193 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Value and significance of brain radiation therapy during first-line EGFR-TKI treatment in lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR sensitive mutation and synchronous brain metastasis: Appropriate timing and technique.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Dec;12(23):3157-3168. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14169. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34651449 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes according to initial and subsequent therapies following intracranial progression in patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancer and brain metastasis.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 16;15(4):e0231546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231546. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32298306 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent EGFR-TKI and Thoracic Radiotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring EGFR Active Mutations.Oncologist. 2019 Aug;24(8):1031-e612. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0285. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 31040256 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparing the efficacy of concurrent EGFR-TKI and whole-brain radiotherapy vs EGFR-TKI alone as a first-line therapy for advanced EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastases: a retrospective cohort study.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Mar 14;11:2129-2138. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S184922. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 30936745 Free PMC article.
-
First-line treatment with TKI plus brain radiotherapy versus TKI alone in EGFR-mutated non-small cell Lung cancer with brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Oct 30;23(1):1043. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11548-0. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37904083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger LA, Riesenberg H, Bokemeyer C, Atanackovic D. CNS metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer: current role of EGFR-TKI therapy and future perspectives. Lung Cancer. 2013;80:242–248. - PubMed
-
- Shin DY, Na II, Kim CH, Park S, Baek H, Yang SH. EGFR mutation and brain metastasis in pulmonary adenocarcinomas. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9:195–199. - PubMed
-
- Khuntia D, Brown P, Li J, Mehta MP. Whole-brain radiotherapy in the management of brain metastasis. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1295–1304. - PubMed
-
- Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:419–425. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sperduto PW, Yang TJ, Beal K, Pan H, Brown PD, Bangdiwala A, Shanley R, Yeh N, Gaspar LE, Braunstein S, Sneed P, Boyle J, Kirkpatrick JP, et al. Estimating survival in patients with lung cancer and brain metastases: an update of the graded prognostic assessment for lung cancer using molecular markers (Lung-molGPA) JAMA Oncol. 2016 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

