High glucose enhances the metastatic potential of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via the PKM2 pathway
- PMID: 29340090
- PMCID: PMC5762358
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.22907
High glucose enhances the metastatic potential of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via the PKM2 pathway
Abstract
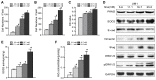
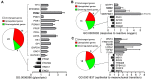
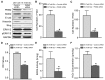
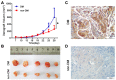
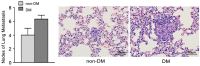
Previous evidence has indicated an increased cancer risk in individuals with diabetes mellitus (DM). The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between DM (high glucose) and tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) and how high glucose mediated the metastatic potential of TSCC. The relationship between DM and TSCC was assessed in a retrospective study. The role and its mechanism of high glucose on the proliferation, metastatic potential of TSCC were investigated in vitro and in vivo. The prevalence rate of DM in patients with TSCC was 12.84%, which was significantly higher than that (9.7%) in the general population in China. Although no significant difference was observed in the overall survival (OS) rate, TSCC patients with DM have a 1.38-fold increase in relative risk affecting 5-year OS compared to patients without DM. High glucose enhanced the TSCC cell proliferation, migration, invasion and upregulated PKM2 (pyruvate kinase M2) expression. Whereas, these effect was abolished after knockdown of PKM2 in TSCC cells. High glucose promoted tumour growth and lung metastasis of TSCC in a DM animal model. Our results confirm DM as a risk factor for the development of TSCC. High glucose enhances the metastatic potential of TSCC through stimulation of the PKM2 pathway.
Keywords: PKM2; high glucose; metastasis; tongue squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pyruvate kinase M2 deregulation enhances the metastatic potential of tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 17;8(40):68252-68262. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19291. eCollection 2017 Sep 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28978113 Free PMC article.
-
Hexokinase 2 enhances the metastatic potential of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via the SOD2-H2O2 pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):3344-3354. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13763. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27926482 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 promotes the growth of tongue squamous cell carcinoma through the microRNA 513c-5p/cell division cycle 25B pathway and is associated with a poor prognosis.Cancer. 2022 May 1;128(9):1775-1786. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34136. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35143052 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of metabolic markers PKM2 and LDH5 correlates with aggressive clinicopathological features and adverse patient prognosis in tongue cancer.Histopathology. 2014 Nov;65(5):595-605. doi: 10.1111/his.12441. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Histopathology. 2014. PMID: 24762230
-
Therapeutic Potential of siRNAs in Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Modulating The PI3K/AKT and ERK Signaling Pathways: A Systematic Review.Cell J. 2024 Aug 11;26(6):337-350. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2024.2021962.1501. Cell J. 2024. PMID: 39154234
Cited by
-
Hyperglycemia induces PFKFB3 overexpression and promotes malignant phenotype of breast cancer through RAS/MAPK activation.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Mar 28;21(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-02990-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36973739 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma stage: an almost loss of fatty acid metabolism and gain of glucose metabolic pathways dysregulation.Med Oncol. 2022 Oct 8;39(12):247. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01839-0. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36209296
-
Hyperglycemia promotes Snail-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer via activating ENO1 expression.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Dec 19;19:344. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-1075-8. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31889896 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of physiological media on acute myeloid leukemia bioenergetics and cell proliferation.Cancer Metab. 2025 May 26;13(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40170-025-00395-1. Cancer Metab. 2025. PMID: 40420205 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia induces miR-26-5p down-regulation to overexpress PFKFB3 and accelerate epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):2902-2917. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2026730. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35094634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J, Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, Zhu D, Ge J, Lin L, et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1090–1101. - PubMed
-
- Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, Bergenstal RM, Gapstur SM, Habel LA, Pollak M, Regensteiner JG, Yee D. Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:207–221. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

