Randomized Clinical Trial Design to Assess Abatacept in Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome
- PMID: 29340321
- PMCID: PMC5762951
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2017.08.013
Randomized Clinical Trial Design to Assess Abatacept in Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome
Abstract
Introduction: Treatment-resistant nephrotic syndrome is a rare form of glomerular disease that occurs in children and adults. No Food and Drug Administration-approved treatments consistently achieve remission of proteinuria and preservation of kidney function. CD80 (B7-1) can be expressed on injured podocytes, and administration of abatacept (modified CTLA4-Ig based on a natural ligand to CD80) has been associated with sustained normalization of urinary protein excretion and maintenance of glomerular filtration rate in experimental and clinical settings.
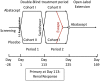
Methods: In this report, we describe the rationale for and design of a randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of abatacept in patients with treatment-resistant nephrotic syndrome caused by focal segmental glomerulosclerosis or minimal change disease. The design is a hybrid of a parallel-group and crossover design (switchover) with the primary objectives assessed in the first period of the study and the secondary objectives assessed using data from both periods. All participants will receive the active agent in 1 of the periods. The duration of treatment will be 4 months per period.
Results: The primary outcome will be improvement in nephrotic-range proteinuria to subnephrotic range, that is, reduction from baseline to 4 months in urine protein:creatinine ratio ≥ 50% and to a level < 3. The projected sample size is 90 patients, which has 80% power to detect a treatment difference of 28%.
Conclusion: This study advances efforts to validate CD80 as a therapeutic target for treatment-resistant nephrotic syndrome, and implements a precision medicine-based approach to this serious kidney condition in which the selection of a therapeutic agent is guided by the underlying disease mechanism operating in individual patients.
Keywords: albuminuria; chronic kidney disease; glomerular disease; podocyte; proteinuria.
Figures
References
-
- D’Agati V.D., Kaskel F.J., Falk R.J. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2398–2411. - PubMed
-
- Beck L., Bomback A.S., Choi M.J. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62:403–441. - PubMed
-
- Trachtman R., Sran S.S., Trachtman H. Recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after kidney transplantation. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015;30:1793–1802. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

