Pharmacokinetics of rituximab and clinical outcomes in patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody associated vasculitis
- PMID: 29340623
- PMCID: PMC5888934
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex484
Pharmacokinetics of rituximab and clinical outcomes in patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody associated vasculitis
Abstract
Objectives: To study the determinants of the pharmacokinetics (PK) of rituximab (RTX) in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) and its association with clinical outcomes.
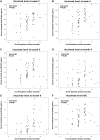
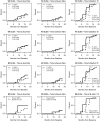
Methods: This study included data from 89 patients from the RTX in AAV trial who received the full dose of RTX (four weekly infusions of 375 mg/m2). RTX was quantified at weeks 2, 4, 8, 16 and 24, and summarized by computing the trapezoidal area under the curve. We explored potential determinants of the PK-RTX, and analysed its association with clinical outcomes: achievement of remission at 6 months, duration of B-cell depletion and time to relapse in patients who achieved complete remission.
Results: RTX serum levels were significantly lower in males and in newly diagnosed patients, and negatively correlated with body surface area, baseline B-cell count and degree of disease activity. In multivariate analyses, the main determinants of PK-RTX were sex and new diagnosis. Patients reaching complete remission at month 6 had similar RTX levels compared with patients who did not reach complete remission. Patients with higher RTX levels generally experienced longer B-cell depletion than patients with lower levels, but RTX levels at the different time points and area under the curve were not associated with time to relapse.
Conclusion: Despite the body-surface-area-based dosing protocol, PK-RTX is highly variable among patients with AAV, its main determinants being sex and newly diagnosed disease. We did not observe any relevant association between PK-RTX and clinical outcomes. The monitoring of serum RTX levels does not seem clinically useful in AAV.
Figures
Similar articles
-
B cell-driven reduced-dose rituximab as induction therapy for 2 patients with ANCA-associated renal vasculitis: A case series.Clin Nephrol. 2025 Feb;103(2):140-147. doi: 10.5414/CN111372. Clin Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39635728
-
Highly Sensitive Flow Cytometric Detection of Residual B-Cells After Rituximab in Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies-Associated Vasculitis Patients.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 15;11:566732. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.566732. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33384685 Free PMC article.
-
The association of serum interleukin-6 levels with clinical outcomes in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis.J Autoimmun. 2019 Dec;105:102302. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.07.001. Epub 2019 Jul 15. J Autoimmun. 2019. PMID: 31320177 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of rituximab trials on the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014 Jun;29(6):1151-9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft318. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014. PMID: 24126571 Review.
-
B-cell-targeted therapy in systemic vasculitis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016 Jan;28(1):15-20. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000235. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26599379 Review.
Cited by
-
Dose-dependent Pharmacological Response to Rituximab in the Treatment of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-associated Vasculitis.J Rheumatol. 2021 Nov;48(11):1718-1724. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.210361. Epub 2021 Aug 1. J Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34334366 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of rituximab pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic alterations in various immune-mediated glomerulopathies and potential anti-CD20 therapy alternatives.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 7;13:1024068. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1024068. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36420256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody Drug Clearance: An Underexplored Marker of Outcomes with Checkpoint Inhibitors.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Mar 1;30(5):942-958. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-1683. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 37921739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rituximab Associated Hypogammaglobulinemia in Autoimmune Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 May 12;12:671503. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.671503. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054846 Free PMC article.
-
Low dose versus standard dose rituximab for the treatment of antiphospholipid syndrome: A pilot study from a tertiary medical center.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 3;13:971366. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.971366. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36405743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA. et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum 2013;65:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Cornec D, Cornec-Le Gall E, Fervenza FC, Specks U.. ANCA-associated vasculitis – clinical utility of using ANCA specificity to classify patients. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2016;12:570–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

