Development of a High-Sensitivity Wireless Accelerometer for Structural Health Monitoring
- PMID: 29342102
- PMCID: PMC5795593
- DOI: 10.3390/s18010262
Development of a High-Sensitivity Wireless Accelerometer for Structural Health Monitoring
Abstract
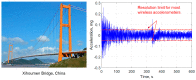
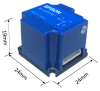
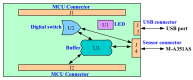
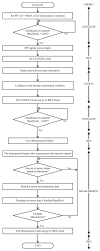
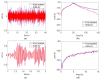
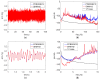
Structural health monitoring (SHM) is playing an increasingly important role in ensuring the safety of structures. A shift of SHM research away from traditional wired methods toward the use of wireless smart sensors (WSS) has been motivated by the attractive features of wireless smart sensor networks (WSSN). The progress achieved in Micro Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) technologies and wireless data transmission, has extended the effectiveness and range of applicability of WSSNs. One of the most common sensors employed in SHM strategies is the accelerometer; however, most accelerometers in WSS nodes have inadequate resolution for measurement of the typical accelerations found in many SHM applications. In this study, a high-resolution and low-noise tri-axial digital MEMS accelerometer is incorporated in a next-generation WSS platform, the Xnode. In addition to meeting the acceleration sensing demands of large-scale civil infrastructure applications, this new WSS node provides powerful hardware and a robust software framework to enable edge computing that can deliver actionable information. Hardware and software integration challenges are presented, and the associate resolutions are discussed. The performance of the wireless accelerometer is demonstrated experimentally through comparison with high-sensitivity wired accelerometers. This new high-sensitivity wireless accelerometer will extend the use of WSSN to a broader class of SHM applications.
Keywords: high-sensitivity accelerometer; structural health monitoring; wireless smart sensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Kim S., Pakzad S., Culler D.E., Demmel J., Fenves G., Glaser S., Turon M. Health monitoring of civil infrastructures using wireless sensor networks; Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, 2007, IPSN 2007; Cambridge, MA, USA. 25–27 April 2007.
-
- Fortino G., Guerrieri A., O’Hare G.M.P., Ruzzelli A. A flexible building management framework based on wireless sensor and actuator networks. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2012;35:1934–1952. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2012.07.016. - DOI
-
- Balageas D., Fritzen C.P., Gemes A. Structural Health Monitoring. Wiley; London, UK: 2006. Introduction to structural health monitoring.
-
- Wong K.Y. Instrumentation and health monitoring of cable-supported bridges. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2004;11:91–124. doi: 10.1002/stc.33. - DOI
-
- Li S., Laima S., Li H. Cluster analysis of winds and wind-induced vibrations on a long-span bridge based on long-term field monitoring data. Eng. Struct. 2017;138:245–259. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.02.024. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

