Adrenergic Agonists Bind to Adrenergic-Receptor-Like Regions of the Mu Opioid Receptor, Enhancing Morphine and Methionine-Enkephalin Binding: A New Approach to "Biased Opioids"?
- PMID: 29342106
- PMCID: PMC5796218
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19010272
Adrenergic Agonists Bind to Adrenergic-Receptor-Like Regions of the Mu Opioid Receptor, Enhancing Morphine and Methionine-Enkephalin Binding: A New Approach to "Biased Opioids"?
Abstract
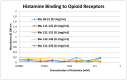
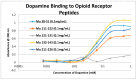
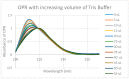
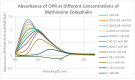
Extensive evidence demonstrates functional interactions between the adrenergic and opioid systems in a diversity of tissues and organs. While some effects are due to receptor and second messenger cross-talk, recent research has revealed an extracellular, allosteric opioid binding site on adrenergic receptors that enhances adrenergic activity and its duration. The present research addresses whether opioid receptors may have an equivalent extracellular, allosteric adrenergic binding site that has similar enhancing effects on opioid binding. Comparison of adrenergic and opioid receptor sequences revealed that these receptors share very significant regions of similarity, particularly in some of the extracellular and transmembrane regions associated with adrenergic binding in the adrenergic receptors. Five of these shared regions from the mu opioid receptor (muOPR) were synthesized as peptides and tested for binding to adrenergic, opioid and control compounds using ultraviolet spectroscopy. Adrenergic compounds bound to several of these muOPR peptides with low micromolar affinity while acetylcholine, histamine and various adrenergic antagonists did not. Similar studies were then conducted with purified, intact muOPR with similar results. Combinations of epinephrine with methionine enkephalin or morphine increased the binding of both by about half a log unit. These results suggest that muOPR may be allosterically enhanced by adrenergic agonists.
Keywords: allosteric; biased opioids; dimerization; enhancement; epinephrine; methionine-enkephalin; morphine; mu opioid receptor; norepinephrine; receptor dimers; synergy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


















Similar articles
-
Glutathione and Glutathione-Like Sequences of Opioid and Aminergic Receptors Bind Ascorbic Acid, Adrenergic and Opioid Drugs Mediating Antioxidant Function: Relevance for Anesthesia and Abuse.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 28;21(17):6230. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176230. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32872204 Free PMC article.
-
Biased, Bitopic, Opioid-Adrenergic Tethered Compounds May Improve Specificity, Lower Dosage and Enhance Agonist or Antagonist Function with Reduced Risk of Tolerance and Addiction.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Feb 10;15(2):214. doi: 10.3390/ph15020214. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delta and mu opioid receptors from the brain of a urodele amphibian, the rough-skinned newt Taricha granulosa: cloning, heterologous expression, and pharmacological characterization.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2006 May 1;146(3):275-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.11.002. Epub 2005 Dec 20. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16375901
-
Similarity of Ca(2+)-bound conformations of morphine and Met-enkephalin: a computational study.FEBS Lett. 1994 Nov 7;354(2):131-4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01071-4. FEBS Lett. 1994. PMID: 7957911
-
Ligands of Adrenergic Receptors: A Structural Point of View.Biomolecules. 2021 Jun 24;11(7):936. doi: 10.3390/biom11070936. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34202543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Individual differences in behavioral effects of xylazine and opioid-xylazine mixtures in male rats.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 27:2025.06.25.661558. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.25.661558. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40667147 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Glutathione and Glutathione-Like Sequences of Opioid and Aminergic Receptors Bind Ascorbic Acid, Adrenergic and Opioid Drugs Mediating Antioxidant Function: Relevance for Anesthesia and Abuse.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 28;21(17):6230. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176230. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32872204 Free PMC article.
-
Biased, Bitopic, Opioid-Adrenergic Tethered Compounds May Improve Specificity, Lower Dosage and Enhance Agonist or Antagonist Function with Reduced Risk of Tolerance and Addiction.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Feb 10;15(2):214. doi: 10.3390/ph15020214. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-Evolution of Opioid and Adrenergic Ligands and Receptors: Shared, Complementary Modules Explain Evolution of Functional Interactions and Suggest Novel Engineering Possibilities.Life (Basel). 2021 Nov 10;11(11):1217. doi: 10.3390/life11111217. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34833093 Free PMC article.
-
Mutual Enhancement of Opioid and Adrenergic Receptors by Combinations of Opioids and Adrenergic Ligands Is Reflected in Molecular Complementarity of Ligands: Drug Development Possibilities.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 24;20(17):4137. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174137. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31450631 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

