Clonal evolution mechanisms in NT5C2 mutant-relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
- PMID: 29342136
- PMCID: PMC5931372
- DOI: 10.1038/nature25186
Clonal evolution mechanisms in NT5C2 mutant-relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
Abstract
Relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is associated with resistance to chemotherapy and poor prognosis. Gain-of-function mutations in the 5'-nucleotidase, cytosolic II (NT5C2) gene induce resistance to 6-mercaptopurine and are selectively present in relapsed ALL. Yet, the mechanisms involved in NT5C2 mutation-driven clonal evolution during the initiation of leukaemia, disease progression and relapse remain unknown. Here we use a conditional-and-inducible leukaemia model to demonstrate that expression of NT5C2(R367Q), a highly prevalent relapsed-ALL NT5C2 mutation, induces resistance to chemotherapy with 6-mercaptopurine at the cost of impaired leukaemia cell growth and leukaemia-initiating cell activity. The loss-of-fitness phenotype of NT5C2+/R367Q mutant cells is associated with excess export of purines to the extracellular space and depletion of the intracellular purine-nucleotide pool. Consequently, blocking guanosine synthesis by inhibition of inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) induced increased cytotoxicity against NT5C2-mutant leukaemia lymphoblasts. These results identify the fitness cost of NT5C2 mutation and resistance to chemotherapy as key evolutionary drivers that shape clonal evolution in relapsed ALL and support a role for IMPDH inhibition in the treatment of ALL.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
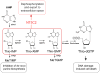
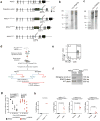
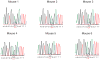
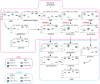





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35 CA210065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA114766/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009503/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA216981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA200651/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008224/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA210607/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA185486/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA209997/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA193313/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA098543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA217858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

