Determination of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) in rat serum for pharmacokinetic studies with a simple HPLC method
- PMID: 29342170
- PMCID: PMC5771594
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191149
Determination of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) in rat serum for pharmacokinetic studies with a simple HPLC method
Abstract
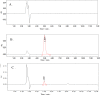
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) is a chlorophenoxy herbicide used worldwide. We describe a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method with UV detection for the determination of 2,4-D in female and male rat serum. This allows to observe the change of serum 2,4-D concentration in rats with time and its pharmacokinetics characteristics with a simple, rapid, optimized and validated method. The serum samples are pretreated and introduced into the HPLC system. The analytes are separated in a XDB-C18 column with a mobile phase of acetonitrile (solvent A) and 0.02 M ammonium acetate (containing 0.1% formic acid) (solvent B) using a gradient elution at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. The wavelength for UV detection was set at 230 nm. Calibration curve for 2,4-D was constructed over a range of 0.1-400 mg/L. The method was successfully applied to study the pharmacokinetics of 2,4-D in rats in this study. After oral administration of 300 mg/kg and 60 mg/kg 2,4-D, the mean Cmax values were 601.9 and 218.4 mg/L, the AUC0→∞ values were 23,722 and 4,127 mg×h/L and the clearance (Cl) were 1.10 and 0.02 L/(h×kg), respectively. The developed method was found to be specific, precise, reproducible and rapid.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Menezes CCD, Loro VL, Fonseca MBD, Cattaneo R, Pretto A, Miron DDS, et al. Oxidative parameters of Rhamdia quelen in response to commercial herbicide containing clomazone and recovery pattern. Pesticide Biochemistry & Physiology. 2011;100(2):145–50.
-
- Munro IC, Carlo GL, Orr JC, Sund KG, Wilson RM, Kennepohl E, et al. A Comprehensive, Integrated Review and Evaluation of the Scientific Evidence Relating to the Safety of the Herbicide 2,4-D. International Journal of Toxicology. 1992;11(5):559–664.
-
- Oghabian Z, Ghanbarzadeh N, Sharifi MD, Mehrpour O. Treatment of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) poisoning; A case study. International Journal of Medical Toxicology & Forensic Medicine. 2014;4(3):104–7.
-
- Obidike IR, Aka LO, Omoja VU, Shoyinka SVO, Kamalu TN, Anika SM. Testicular morphology and antispermatogenic effects of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) in male West African Dwarf (WAD) goats. Comparative Clinical Pathology. 2011;21(6):1457–62.
-
- Tayeb W, Nakbi A, Trabelsi M, Miled A, Hammami M. Biochemical and histological evaluation of kidney damage after sub-acute exposure to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic herbicide in rats: involvement of oxidative stress. Toxicology Mechanisms & Methods. 2012;22(9):696–704. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

