Associations of Quadriceps Torque Properties with Muscle Size, Attenuation, and Intramuscular Adipose Tissue in Older Adults
- PMID: 29342246
- PMCID: PMC6001898
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glx262
Associations of Quadriceps Torque Properties with Muscle Size, Attenuation, and Intramuscular Adipose Tissue in Older Adults
Abstract
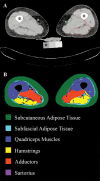
Background: Atrophy and fatty infiltration of muscle with aging are associated with fractures and falls, however, their direct associations with muscle function are not well described. It was hypothesized that participants with lower quadriceps muscle attenuation, area, and greater intramuscular adipose tissue (IMAT) will exhibit slower rates of torque development (RTD) and lower peak knee extension torques.
Methods: Data from 4,842 participants (2,041 men, 2,801 women) from the Age Gene/Environment Susceptibility Reykjavik Study (mean age 76 ± 0.1 years) with complete thigh computed tomography and isometric knee testing. Regression models were adjusted for health, behavior, and comorbidities. Muscle attenuation was further adjusted for muscle area and IMAT; muscle area adjusted for IMAT and attenuation; and IMAT adjusted for muscle area and attenuation. Standardized betas (β) indicate association effect sizes.
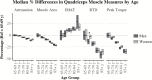
Results: In the fully-adjusted models, attenuation (men β = 0.06, 95% CI: 0.01, 0.11; women β = 0.07, 95% CI: 0.03, 0.11) and muscle area (men β = 0.13, 95% CI: 0.07, 0.19; women β = 0.10, 95% CI: 0.06, 0.15) were associated with knee RTD. Attenuation (men β = 0.12, 95% CI: 0.08, 0.16; women β = 0.12, 95% CI: 0.09, 0.16) and muscle area (men β = 0.38, 95% CI: 0.33, 0.43; women β = 0.33, 95% CI: 0.29, 0.37) were associated with peak torque.
Conclusions: These data suggest that muscle attenuation and area are independently associated with RTD and peak torque; and that area and attenuation demonstrate similar contributions to RTD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cigarette Smoking Is Associated With Lower Quadriceps Cross-sectional Area and Attenuation in Older Adults.Nicotine Tob Res. 2020 May 26;22(6):935-941. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntz081. Nicotine Tob Res. 2020. PMID: 31091312 Free PMC article.
-
Echo intensity is negatively associated with functional capacity in older women.Age (Dordr). 2014;36(5):9708. doi: 10.1007/s11357-014-9708-2. Epub 2014 Aug 29. Age (Dordr). 2014. PMID: 25167965 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Quadriceps Femoris Muscle Function and MRI-Derived Water Diffusion and Adipose Tissue Measurements in Young Healthy Males.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023 Aug;58(2):548-556. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28525. Epub 2022 Nov 7. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36342320
-
Contribution of Neuromuscular Factors to Quadriceps Asymmetry After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction.J Athl Train. 2018 Apr;53(4):347-354. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-463-16. Epub 2018 Apr 13. J Athl Train. 2018. PMID: 29652169 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Muscle strength, mass, and quality in older men and women with knee osteoarthritis.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012 Jan;64(1):15-21. doi: 10.1002/acr.20588. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22213722 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Quadriceps Lipid Content Has Sex-Specific Associations With Whole-Muscle, Cellular, and Molecular Contractile Function in Older Adults.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2019 Nov 13;74(12):1879-1886. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gly235. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30428006 Free PMC article.
-
The Presence of Myosteatosis Is Associated with Age, Severity of Liver Disease and Poor Outcome and May Represent a Prodromal Phase of Sarcopenia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis.J Clin Med. 2023 May 7;12(9):3332. doi: 10.3390/jcm12093332. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37176772 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning Technique for Automatic Segmentation of Proximal Hip Musculoskeletal Tissues From CT Scan Images: A MrOS Study.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025 Apr;16(2):e13728. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13728. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025. PMID: 40022453 Free PMC article.
-
Early and late rapid torque characteristics and select physiological correlates in middle-aged and older males.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 23;15(4):e0231907. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231907. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32324776 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Fatty Infiltration of Muscle on Falls and Fall-Related Outcomes in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2025 Apr 16;17(4):e82345. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82345. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40385727 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reinders I, Murphy RA, Brouwer IA et al. ; Age, Gene/Environment Susceptibility (AGES)-Reykjavik Study Muscle quality and myosteatosis: novel associations with mortality risk: the Age, Gene/Environment Susceptibility (AGES)-Reykjavik Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2016;183:53–60. doi:10.1093/aje/kwv153 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frank-Wilson AW, Farthing JP, Chilibeck PD et al. . Lower leg muscle density is independently associated with fall status in community-dwelling older adults. Osteoporos Int. 2016. Jul;27(7):2231–2240. doi:10.1007/s00198-016-3514-x. Epub 2016 Feb 15 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

