Small Peptides Able to Suppress Prostaglandin E₂ Generation in Renal Mesangial Cells
- PMID: 29342835
- PMCID: PMC6017359
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23010158
Small Peptides Able to Suppress Prostaglandin E₂ Generation in Renal Mesangial Cells
Abstract
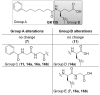
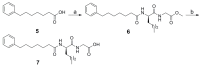
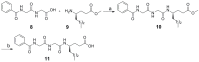
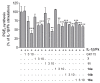
Peptide drug discovery may play a key role in the identification of novel medicinal agents. Here, we present the development of novel small peptides able to suppress the production of PGE₂ in mesangial cells. The new compounds were generated by structural alterations applied on GK115, a novel inhibitor of secreted phospholipase A₂, which has been previously shown to reduce PGE₂ synthesis in rat renal mesangial cells. Among the synthesized compounds, the tripeptide derivative 11 exhibited a nice dose-dependent suppression of PGE₂ production, similar to that observed for GK115.
Keywords: inhibitors; mesangial cells; peptides; prostaglandin E2; secreted phospholipase A2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Sterzel R.B., Schulze-Lohoff E., Marx M. Cytokines and mesangial cells. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1993;39:S26–S31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

