Hypoxia and Hormone-Mediated Pathways Converge at the Histone Demethylase KDM4B in Cancer
- PMID: 29342868
- PMCID: PMC5796188
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19010240
Hypoxia and Hormone-Mediated Pathways Converge at the Histone Demethylase KDM4B in Cancer
Abstract
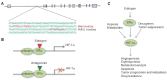
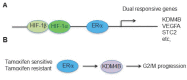
Hormones play an important role in pathophysiology. The hormone receptors, such as estrogen receptor alpha and androgen receptor in breast cancer and prostate cancer, are critical to cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth. In this review we focused on the cross-talk between hormone and hypoxia pathways, particularly in breast cancer. We delineated a novel signaling pathway from estrogen receptor to hypoxia-inducible factor 1, and discussed the role of this pathway in endocrine therapy resistance. Further, we discussed the estrogen and hypoxia pathways converging at histone demethylase KDM4B, an important epigenetic modifier in cancer.
Keywords: KDM4B; endocrine therapy resistance; estrogen receptor alpha; hypoxia-inducible factor 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting the KDM4B-AR-c-Myc axis promotes sensitivity to androgen receptor-targeted therapy in advanced prostate cancer.J Pathol. 2020 Oct;252(2):101-113. doi: 10.1002/path.5495. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32617978
-
The histone demethylase JMJD2B is regulated by estrogen receptor alpha and hypoxia, and is a key mediator of estrogen induced growth.Cancer Res. 2010 Aug 15;70(16):6456-66. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0413. Epub 2010 Aug 3. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20682797 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting KDM4B that coactivates c-Myc-regulated metabolism to suppress tumor growth in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Theranostics. 2021 Jun 26;11(16):7779-7796. doi: 10.7150/thno.58729. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34335964 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into The Function and Regulation of Jumonji C Lysine Demethylases as Hypoxic Responsive Enzymes.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020;21(7):642-654. doi: 10.2174/1389203721666191231104225. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020. PMID: 31889485 Review.
-
KDM4B: A promising oncology therapeutic target.Cancer Sci. 2024 Jan;115(1):8-16. doi: 10.1111/cas.16005. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 37923555 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
KDM4B: A Nail for Every Hammer?Genes (Basel). 2019 Feb 12;10(2):134. doi: 10.3390/genes10020134. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30759871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H19-Dependent Transcriptional Regulation of β3 and β4 Integrins Upon Estrogen and Hypoxia Favors Metastatic Potential in Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 17;20(16):4012. doi: 10.3390/ijms20164012. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31426484 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding human aging and the fundamental cell signaling link in age-related diseases: the middle-aging hypovascularity hypoxia hypothesis.Front Aging. 2023 Jun 13;4:1196648. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2023.1196648. eCollection 2023. Front Aging. 2023. PMID: 37384143 Free PMC article.
-
The Histone Demethylase Enzymes KDM3A and KDM4B Co-Operatively Regulate Chromatin Transactions of the Estrogen Receptor in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 6;11(8):1122. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081122. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31390833 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted Interplay between Hormones, Growth Factors and Hypoxia in the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 21;14(3):539. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030539. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158804 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jaakkola P., Mole D.R., Tian Y.M., Wilson M.I., Gielbert J., Gaskell S.J., von Kriegsheim A., Hebestreit H.F., Mukherji M., Schofield C.J., et al. Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science. 2001;292:468–472. doi: 10.1126/science.1059796. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

