Lapatinib Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation by Influencing PKM2 Expression
- PMID: 29343208
- PMCID: PMC5784572
- DOI: 10.1177/1533034617749418
Lapatinib Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation by Influencing PKM2 Expression
Abstract
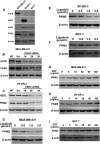
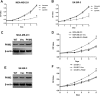
Pyruvate kinase type M2, which is expressed in multiple tumor cell types and plays a key role in aerobic glycolysis, also has nonglycolytic functions and can regulate transcription and cell proliferation. The results of this study show that epidermal growth factor receptor activation induces pyruvate kinase type M2 nuclear translocation. To further determine the relationship between pyruvate kinase type M2 and epidermal growth factor receptor, we analyzed pathological data from mammary glands and performed epidermal growth factor receptor/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 knockdown to reveal that pyruvate kinase type M2 is associated with epidermal growth factor receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. Lapatinib is a small molecule epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that can inhibit epidermal growth factor receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, though its effect on pyruvate kinase type M2 remains elusive. Accordingly, we performed Western blotting and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and analyzed pathological data from mammary glands, with results suggesting that lapatinib inhibits pyruvate kinase type M2 expression. We further found that the antitumor drug lapatinib inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation by influencing pyruvate kinase type M2 expression, as based on Cell Counting Kit-8 analyses and pyruvate kinase type M2 overexpression experiments. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, which is a transcription factor-associated cell proliferation and the only transcription factor that interacts with pyruvate kinase type M2, we performed pyruvate kinase type M2 knockdown experiments in Human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 and Human breast cancer cells SK-BR-3 cell lines and examined the effect on levels of Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and phosphorylated Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. The results indicate that pyruvate kinase type M2 regulates Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and phospho-Stat3 (Tyr705) expression. Together with previous reports, our findings show that lapatinib inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation by influencing pyruvate kinase type M2 expression, which results in a reduction in both Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and phosphorylated Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
Keywords: breast cancer; cell proliferation; isoenzyme; lapatinib; pyruvate kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of pyruvate kinase M2 isoform inhibits cell motility in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Aug 14;21(30):9093-102. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9093. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26290635 Free PMC article.
-
PKM2 promotes glucose metabolism through a let-7a-5p/Stat3/hnRNP-A1 regulatory feedback loop in breast cancer cells.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):6542-6554. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27947. Epub 2018 Oct 28. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30368881
-
Niclosamide inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor growth in lapatinib-resistant human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Feb;71:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.11.014. Epub 2015 Nov 28. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26643609
-
Recent Advances on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor as a Molecular Target for Breast Cancer Therapeutics.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(14):1783-1792. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666201222143213. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33355057 Review.
-
Lapatinib: a small-molecule inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinases used in the treatment of breast cancer.Clin Ther. 2009;31 Pt 2:2332-48. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.11.029. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 20110044 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic changes in triple negative breast cancer-focus on aerobic glycolysis.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 May;48(5):4733-4745. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06414-w. Epub 2021 May 28. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34047880 Review.
-
Effects of Lapatinib on HER2-Positive and HER2-Negative Canine Mammary Carcinoma Cells Cultured In Vitro.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 17;13(6):897. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060897. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34204236 Free PMC article.
-
In silico predictions on the possible mechanism of action of selected bioactive compounds against breast cancer.In Silico Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 9;8(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s40203-020-00057-8. eCollection 2020. In Silico Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33194532 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-EGFR/BRAF-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Thyroid Carcinoma.Cancer Diagn Progn. 2023 Mar 3;3(2):151-156. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10194. eCollection 2023 Mar-Apr. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2023. PMID: 36875315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STAT3 pathway in cancers: Past, present, and future.MedComm (2020). 2022 Mar 23;3(2):e124. doi: 10.1002/mco2.124. eCollection 2022 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 35356799 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH, et al. The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature. 2008;452(7184):230–233. doi:10.1038/nature06734. - PubMed
-
- Mazurek S. Pyruvate kinase type M2: a key regulator of the metabolic budget system in tumor cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011;43(7):969–980. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2010.02.005. - PubMed
-
- Mazurek S, Boschek CB, Hugo F, Eigenbrodt E. Pyruvate kinase type M2 and its role in tumor growth and spreading. Semin Cancer Biol. 2005;15(4):300–308. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2005.04.009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

