What motivates medical students to select medical studies: a systematic literature review
- PMID: 29343262
- PMCID: PMC5772649
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-018-1123-4
What motivates medical students to select medical studies: a systematic literature review
Abstract
Background: There is a significant shortage of health workers across and within countries. It is of utmost importance to determine the factors that motivate students to opt for medical studies. The objective of this study is to group and review all the studies that investigated the motivational factors that underpin students' selection of medical study in recent years.
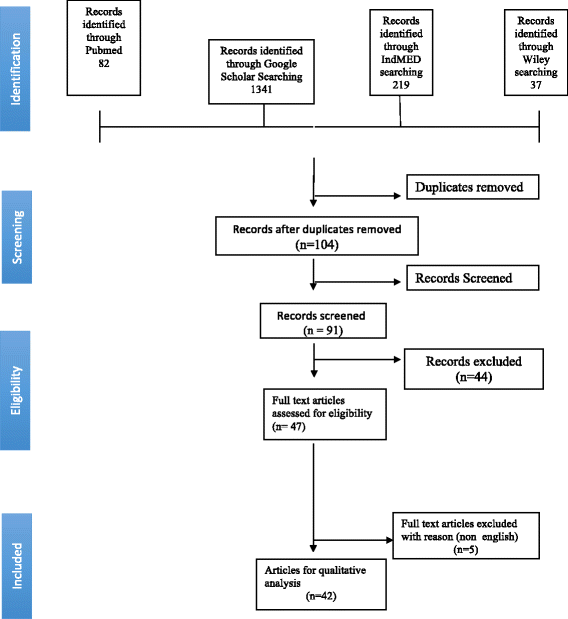
Methods: The literature search was carried out by two researchers independently in PubMed, Google Scholar, Wiley and IndMED databases for articles published from year 2006 till 2016. A total of 38 combinations of MeSH words were used for search purpose. Studies related to medical students and interns have been included. The application of inclusion and exclusion criteria and PRISMA guidelines for reporting systematic review led to the final selection of 24 articles.
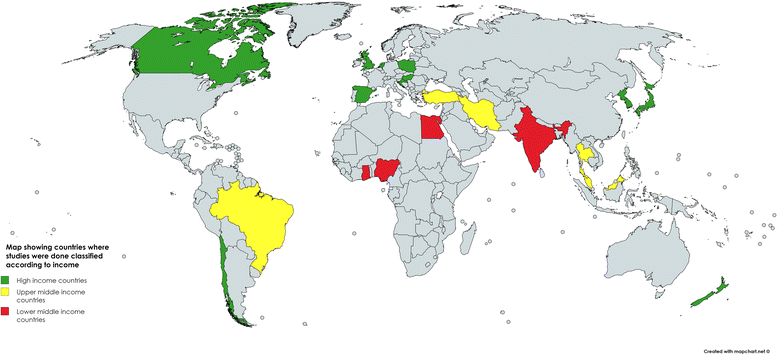
Results: The majority of the studies (n = 16; 66.6%) were from high-income countries followed by an equal number from upper-middle and lower-middle income countries (n = 4,16.7%). None of the studies were from low-income countries. All of the studies were cross-sectional in nature. The main motivating factors that emerged were scientific (interest in science / medicine, social interest and academia, flexible work hours and work independence), societal (prestige, job security, financial security) and humanitarian (serving the poor and under priviledged) in high-, upper-middle and lower-middle income countries, respectively. The findings were comparable to Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory of motivation.
Conclusion: This systematic review identifies the motivational factors influencing students to join medical studies in different parts of the globe. These factors vary per country depending on the level of income. This study offers cues to policy makers and educators to formulate policy in order to tackle the shortage of health workers, i.e. medical doctors. However, more research is needed to translate health policy into concrete and effective measures.
Keywords: Medical students; Motivation; Rural areas; Systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was granted ethical approval from the Institute’s Ethical Committee, PGIMER, Chandigarh (PGI/IEC/2012/810–1 P-154). The anonymity and confidentiality of participants in the studies were ensured. Since the study is a systematic review of studies and individual level data is not obtained, the consent was not required.
Consent for publication
Since individual level data is not presented, the consent for publication of data was not required.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. The world health report 2006: working together for health. Geneva: WHO; 2006 [Internet]. 2015. Available from: http://www.who.int/whr/2006/en/. Accessed 12 Oct 2015.
-
- Campbell J, Dussault G, Buchan J, Pozo-Martin F, Guerra Arias M, Leone C, Siyam A, Cometto G. A universal truth: no health without a workforce. Forum Report, Third Global Forum on Human Resources for Health, Recife, Brazil. Geneva: Global Health Workforce Alliance and World Health Organization; 2013.
-
- Rao K, Bhatnagar A, Berman P. India’s health workforce: size, composition and distribution. In: La Forgia KR J, editor. India health beat. New Delhi: World Bank; New Delhi and Public Health Foundation of India; 2009.
-
- Hurst SA. Eroding students’ rural motivation: first do no harm? Swiss Med Wkly. 2014;144 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

