Regulation of the Immune Response by the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor
- PMID: 29343438
- PMCID: PMC5777317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.12.012
Regulation of the Immune Response by the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor
Abstract
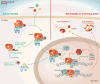
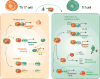
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor that is activated by small molecules provided by the diet, microorganisms, metabolism, and pollutants. AhR is expressed by a number of immune cells, and thus AhR signaling provides a molecular pathway that integrates the effects of the environment and metabolism on the immune response. Studies have shown that AhR signaling plays important roles in the immune system in health and disease. As its activity is regulated by small molecules, AhR also constitutes a potential target for therapeutic immunomodulation. In this review we discuss the role of AhR in the regulation of the immune response in the context of autoimmunity, infection, and cancer, as well as the potential opportunities and challenges of developing AhR-targeted therapeutics.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adachi J, Mori Y, Matsui S, Takigami H, Fujino J, Kitagawa H, Miller CA, 3rd, Kato T, Saeki K, Matsuda T. Indirubin and indigo are potent aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands present in human urine. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:31475–31478. - PubMed
-
- Awasthi A, Carrier Y, Peron JP, Bettelli E, Kamanaka M, Flavell RA, Kuchroo VK, Oukka M, Weiner HL. A dominant function for interleukin 27 in generating interleukin 10-producing anti-inflammatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:1380–1389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

