Circular RNA VMA21 protects against intervertebral disc degeneration through targeting miR-200c and X linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein
- PMID: 29343508
- PMCID: PMC5909753
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212056
Circular RNA VMA21 protects against intervertebral disc degeneration through targeting miR-200c and X linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein
Abstract
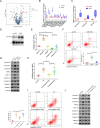
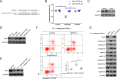
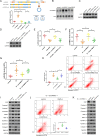
Objectives: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been proven to function as competing endogenous RNAs to interact with microRNAs (miRNAs) and influence the expression of miRNA target mRNAs. In this study, we investigated whether circRNAs could act as competing endogenous RNAs to regulate the pathological process of intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD).
Methods: The role and mechanism of a circRNA, circVMA21, in IVDD were explored in nucleus pulposus (NP) cells and degenerative NP tissues from patients and rat models. The interaction between circVMA21 and miR-200c as well as the target mRNA, X linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein (XIAP), was examined.
Results: The decreased expression of XIAP in the inflammatory cytokines-treated NP cells and the degenerative NP tissues was directly associated with excessive apoptosis and imbalance between anabolic and catabolic factors of extracellular matrix. miR-200c regulated NP cell viability and functions through inhibiting XIAP. circVMA21 acted as a sponge of miR-200c and functioned in NP cells through targeting miR-200c and XIAP. Intradiscal injection of circVMA21 alleviated IVDD in the rat model.
Conclusions: CircVMA21 could alleviate inflammatory cytokines-induced NP cell apoptosis and imbalance between anabolism and catabolism of extracellular matrix through miR-200c-XIAP pathway. It provides a potentially effective therapeutic strategy for IVDD.
Keywords: cytokines; inflammation; low back pain; osteoarthritis; tnf-alpha.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



Comment in
-
Degenerative disc disease: Circular RNA reduces cell death in IVD disease.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018 Mar;14(3):123. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2018.13. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29416131 No abstract available.
References
-
- GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016;388:1545–602. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

