PAR1 agonists stimulate APC-like endothelial cytoprotection and confer resistance to thromboinflammatory injury
- PMID: 29343648
- PMCID: PMC5798377
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1718600115
PAR1 agonists stimulate APC-like endothelial cytoprotection and confer resistance to thromboinflammatory injury
Abstract
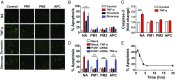
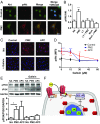
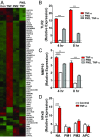
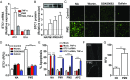
Stimulation of protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1) on endothelium by activated protein C (APC) is protective in several animal models of disease, and APC has been used clinically in severe sepsis and wound healing. Clinical use of APC, however, is limited by its immunogenicity and its anticoagulant activity. We show that a class of small molecules termed "parmodulins" that act at the cytosolic face of PAR1 stimulates APC-like cytoprotective signaling in endothelium. Parmodulins block thrombin generation in response to inflammatory mediators and inhibit platelet accumulation on endothelium cultured under flow. Evaluation of the antithrombotic mechanism showed that parmodulins induce cytoprotective signaling through Gβγ, activating a PI3K/Akt pathway and eliciting a genetic program that includes suppression of NF-κB-mediated transcriptional activation and up-regulation of select cytoprotective transcripts. STC1 is among the up-regulated transcripts, and knockdown of stanniocalin-1 blocks the protective effects of both parmodulins and APC. Induction of this signaling pathway in vivo protects against thromboinflammatory injury in blood vessels. Small-molecule activation of endothelial cytoprotection through PAR1 represents an approach for treatment of thromboinflammatory disease and provides proof-of-principle for the strategy of targeting the cytoplasmic surface of GPCRs to achieve pathway selective signaling.
Keywords: PAR1; cytoprotection; endothelium; inflammation; thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: R.F. and C.D. are inventors on a patent describing parmodulins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Parmodulins inhibit thrombus formation without inducing endothelial injury caused by vorapaxar.Blood. 2015 Mar 19;125(12):1976-85. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-09-599910. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25587041 Free PMC article.
-
A novel protein C-factor VII chimera provides new insights into the structural requirements for cytoprotective protease-activated receptor 1 signaling.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Nov;15(11):2198-2207. doi: 10.1111/jth.13807. Epub 2017 Sep 21. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28834159
-
Occupancy of human EPCR by protein C induces β-arrestin-2 biased PAR1 signaling by both APC and thrombin.Blood. 2016 Oct 6;128(14):1884-1893. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-06-720581. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27561318 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting biased signaling by PAR1: function and molecular mechanism of parmodulins.Blood. 2023 Jun 1;141(22):2675-2684. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023019775. Blood. 2023. PMID: 36952648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New Concept of Action of Hemostatic Proteases on Inflammation, Neurotoxicity, and Tissue Regeneration.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2017 Jul;82(7):778-790. doi: 10.1134/S0006297917070033. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2017. PMID: 28918742 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypercoagulability Impairs Plaque Stability in Diabetes-Induced Atherosclerosis.Nutrients. 2022 May 10;14(10):1991. doi: 10.3390/nu14101991. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35631132 Free PMC article.
-
Complement and Coagulation System Crosstalk in Synaptic and Neural Conduction in the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems.Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 20;9(12):1950. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121950. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34944766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antagonizing the irreversible thrombomodulin-initiated proteolytic signaling alleviates age-related liver fibrosis via senescent cell killing.Cell Res. 2023 Jul;33(7):516-532. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00820-4. Epub 2023 May 11. Cell Res. 2023. PMID: 37169907 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Protease-Activated Receptor (PAR) ligands: Parmodulins are reversible allosteric inhibitors of PAR1-driven calcium mobilization in endothelial cells.Bioorg Med Chem. 2018 May 15;26(9):2514-2529. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.04.016. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Bioorg Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29685684 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine interaction with adenosine receptor A2a promotes gastric cancer metastasis by enhancing PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Sep 1;30(19):2527-2534. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E19-03-0136. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31339445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vu TK, Hung DT, Wheaton VI, Coughlin SR. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991;64:1057–1068. - PubMed
-
- Griffin CT, Srinivasan Y, Zheng YW, Huang W, Coughlin SR. A role for thrombin receptor signaling in endothelial cells during embryonic development. Science. 2001;293:1666–1670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

