A new class of magnetically actuated pumps and valves for microfluidic applications
- PMID: 29343852
- PMCID: PMC5772482
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-19506-8
A new class of magnetically actuated pumps and valves for microfluidic applications
Abstract
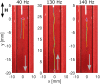
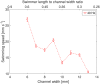
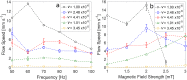
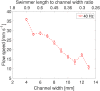
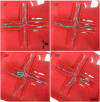
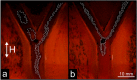
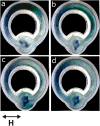
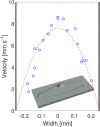
We propose a new class of magnetically actuated pumps and valves that could be incorporated into microfluidic chips with no further external connections. The idea is to repurpose ferromagnetic low Reynolds number swimmers as devices capable of generating fluid flow, by restricting the swimmers' translational degrees of freedom. We experimentally investigate the flow structure generated by a pinned swimmer in different scenarios, such as unrestricted flow around it as well as flow generated in straight, cross-shaped, Y-shaped and circular channels. This demonstrates the feasibility of incorporating the device into a channel and its capability of acting as a pump, valve and flow splitter. Different regimes could be selected by tuning the frequency and amplitude of the external magnetic field driving the swimmer, or by changing the channel orientation with respect to the field. This versatility endows the device with varied functionality which, together with the robust remote control and reproducibility, makes it a promising candidate for several applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Zahn, J. D. Micropump Applications in Bio-MEMS. In. W. Wang, W. & Soper, S. A., Bio-MEMS - Technologies and Applications, CRC Press, vol. 4, 142–176 (2007).
-
- Nikitopoulos, D. E. & Maha, A. Micromixers. In. W. Wang and Soper, S. A. Bio-MEMS - Technologies and Applications, CRC Press, vol. 4, 177–212 (2007).
-
- Au, K, A. Lai, H., Utela, R., B. & Folch, A. A comprehensive study of micropumps technologies. Micromachines2 (2011).
-
- Purcell EM. Life at low Reynolds number. Am. J. Phys. 1977;45:3–11. doi: 10.1119/1.10903. - DOI
-
- Shapere A, Wilczek F. Geometry of self-propulsion at low Reynolds number. J. Fluid Mech. 1989;198:557. doi: 10.1017/S002211208900025X. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

