Combination Therapy with Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers and Vitamin D Receptor Activators for Predialysis Patients Is Associated with the Incidence of Cardiovascular Events after Dialysis Initiation: A Multicenter Nonrandomized Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 29344028
- PMCID: PMC5757592
- DOI: 10.1159/000479894
Combination Therapy with Renin-Angiotensin System Blockers and Vitamin D Receptor Activators for Predialysis Patients Is Associated with the Incidence of Cardiovascular Events after Dialysis Initiation: A Multicenter Nonrandomized Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Several human studies reported that the combined use of renin-angiotensin system blockers (RASBs) and vitamin D receptor activators (VDRAs) resulted in decreased urinary protein excretion. However, it is unknown whether this combination therapy influences the incidence of cardiovascular (CV) events in dialysis patients.
Methods: The study was a multicenter nonrandomized prospective cohort analysis including 1,518 patients. Patients were classified into 4 groups based on medications prescribed before dialysis initiation: those who did not receive RASBs or oral VDRAs (N group), those receiving only RASBs, those receiving only VDRAs, and those receiving a combination of RASBs and VDRAs (RD group). CV events after dialysis initiation were compared using the log-rank test. Factors contributing to the incidence of CV events were examined using multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression analysis.
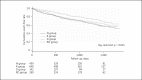
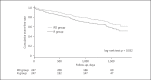
Results: Significant differences were observed in the incidence of CV events and all-cause mortality between the 4 groups (p = 0.021 and p = 0.001, respectively). Cox proportional hazard analysis revealed that the incidence of CV events was significantly lower in the RD group than in the N group (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.65, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.50-0.86, p = 0.002). Multivariate analysis revealed that the incidence of CV events was significantly lower in the RD group than in the N group (HR = 0.66, 95% CI: 0.47-0.93, p = 0.016).
Conclusion: Combination therapy with RASBs and VDRAs in patients before dialysis initiation was associated with a reduction in CV events during maintenance dialysis.
Keywords: Cardiovascular events; Chronic kidney disease; Dialysis; Renin-angiotensin system blocker; Vitamin D; Vitamin D receptor activator.
Figures
References
-
- Konstam MA, Rousseau MF, Kronenberg MW, Udelson JE, Melin J, Stewart D, et al. Effects of the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor enalapril on the long-term progression of left ventricular dysfunction in patients with heart failure. SOLVD Investigators. Circulation. 1992;86:431–438. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg B, Quinones MA, Koilpillai C, Limacher M, Shindler D, Benedict C, et al. Effects of long-term enalapril therapy on cardiac structure and function in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. Results of the SOLVD echocardiography substudy. Circulation. 1995;91:2573–2581. - PubMed
-
- Gullestad L, Aukrust P, Ueland T, Espevik T, Yee G, Vagelos R, et al. Effect of high- versus low-dose angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition on cytokine levels in chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999;34:2061–2067. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
