The Effects of Ginger on Fasting Blood Sugar, Hemoglobin A1c, and Lipid Profiles in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 29344037
- PMCID: PMC5750786
- DOI: 10.5812/ijem.57927
The Effects of Ginger on Fasting Blood Sugar, Hemoglobin A1c, and Lipid Profiles in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Background: Lipid and glycemic abnormalities are prevalent in diabetes leading to long term complications. Use of safe and natural foods instead of medications is now considered by many scientists.
Objectives: This study aimed at determining the effect of ginger on lipid and glucose levels of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods: In a double-blind placebo-controlled trial, 50 patients with type 2 diabetes were randomly allocated to 2 groups of intervention (n = 25) and placebo (n = 25). Each patient received 2000 mg per day of ginger supplements or placebo for 10 weeks. Serum levels of fasting blood sugar (FBS), total cholesterol (TC), triacylglycerol (TG), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) were analyzed. Daily dietary intakes and anthropometric parameters were also determined.
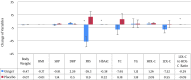
Results: Data from 45 patients were analyzed (23 patients in the ginger group and 22 patients in the control group) at the end of the study. Ginger consumption significantly reduced serum levels of fasting blood glucose (-26.30 ± 35.27 vs. 11.91 ± 38.58 mg/dl; P = 0.001) and hemoglobin A1C (-0.38 ± 0.35 vs. 0.22 ± 0.29 %; P < 0.0001) compared to the placebo group. Ginger consumption also reduced the ratio of LDL-C/HDL-C (2.64 ± 0.85 vs. 2.35 ± 0.8; P = 0.009). However, there was no significant change in serum concentrations of triglycerides, total cholesterol, LDL-C, and HDL-C due to the ginger supplements.
Conclusions: The current results showed that ginger could reduce serum levels of fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1C in patients with diabetes.
Keywords: Blood Sugar; Ginger; HbA1C; Lipid Parameters; Type 2 Diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Kayarohanam S. Current Trends of Plants Having Antidiabetic Activity: A Review. J Bioanalysis Biomed. 2015;07(02) doi: 10.4172/1948-593x.1000124. - DOI
-
- Aguiree F. IDF diabetes atlas. 2013.
-
- Esteghamati A, Gouya MM, Abbasi M, Delavari A, Alikhani S, Alaedini F, et al. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in the adult population of Iran: National Survey of Risk Factors for Non-Communicable Diseases of Iran. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(1):96–8. doi: 10.2337/dc07-0959. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fowler MJ. Microvascular and Macrovascular Complications of Diabetes. Clin Diabetes. 2008;26(2):77–82. doi: 10.2337/diaclin.26.2.77. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous