Whole genome sequencing analysis for cancer genomics and precision medicine
- PMID: 29345757
- PMCID: PMC5834793
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13505
Whole genome sequencing analysis for cancer genomics and precision medicine
Abstract
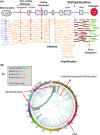
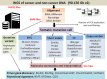
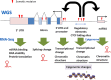
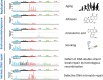
Explosive advances in next-generation sequencer (NGS) and computational analyses have enabled exploration of somatic protein-altered mutations in most cancer types, with coding mutation data intensively accumulated. However, there is limited information on somatic mutations in non-coding regions, including introns, regulatory elements and non-coding RNA. Structural variants and pathogen in cancer genomes remain widely unexplored. Whole genome sequencing (WGS) approaches can be used to comprehensively explore all types of genomic alterations in cancer and help us to better understand the whole landscape of driver mutations and mutational signatures in cancer genomes and elucidate the functional or clinical implications of these unexplored genomic regions and mutational signatures. This review describes recently developed technical approaches for cancer WGS and the future direction of cancer WGS, and discusses its utility and limitations as an analysis platform and for mutation interpretation for cancer genomics and cancer precision medicine. Taking into account the diversity of cancer genomes and phenotypes, interpretation of abundant mutation information from WGS, especially non-coding and structure variants, requires the analysis of large-scale WGS data integrated with RNA-Seq, epigenomics, immuno-genomic and clinic-pathological information.
Keywords: cancer genome; mutational signature; non-coding mutation; structural variant; whole genome sequencing.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
References
-
- Garraway LA, Lander ES. Lessons from the cancer genome. Cell. 2013;153:17‐37. - PubMed
-
- Kinzler KW, Vogetstein B. Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell. 1996;87:159‐170. - PubMed
-
- King CR, Kraus M, Aaronson SA. Amplification of a novel v‐erbB related gene in human mammary carcinoma. Science. 1985;229:974‐976. - PubMed
-
- Meyerson M, Gabriel S, Getz G. Advances in understanding cancer genomes through second‐generation sequencing. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:685‐696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

