Prediction of Hot Spots at Myeloid Cell Leukemia-1-Inhibitor Interface Using Energy Estimation and Alanine Scanning Mutagenesis
- PMID: 29345906
- PMCID: PMC6203182
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01048
Prediction of Hot Spots at Myeloid Cell Leukemia-1-Inhibitor Interface Using Energy Estimation and Alanine Scanning Mutagenesis
Abstract
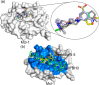
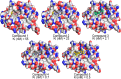
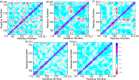
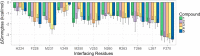
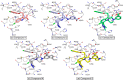
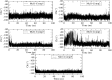
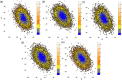
Myeloid cell leukemia 1 (Mcl1) is an antiapoptotic protein that plays central role in apoptosis regulation. Also, Mcl1 has the potency to resist apoptotic cues resulting in up-regulation and cancer cell protection. A molecular probe that has the potential to specifically target Mcl1 and thereby provoke its down-regulatory activity is very essential. The aim of the current study is to probe the internal conformational dynamics of protein motions and potential binding mechanism in response to a series of picomolar range Mcl1 inhibitors using explicit-solvent molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Subsequently, domain cross-correlation and principal component analysis was performed on the snapshots obtained from the MD simulations. Our results showed significant differences in the internal conformational dynamics of Mcl1 with respect to binding affinity values of inhibitors. Further, the binding free energy estimation, using three different samples, was performed on the MD simulations and revealed that the predicted energies (ΔGmmgbsa) were in good correlation with the experimental values (ΔGexpt). Also, the energies obtained using all sampling models were efficiently ranked. Subsequently, the decomposition energy analysis highlighted the major energy-contributing residues at the Mcl1 binding pocket. Computational alanine scanning performed on high energy-contributing residues predicted the hot spot residues. The dihedral angle analysis using MD snapshots on the predicted hot spot residue exhibited consistency in side chain conformational motion that ultimately led to strong binding affinity values. The findings from the present study might provide valuable guidelines for the design of novel Mcl1 inhibitors that might significantly improve the specificity for new-generation chemotherapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






References
-
- Reed J. C.; Miyashita T.; Takayama S.; Wang H. G.; Sato T.; Krajewski S.; Aime-Sempe C.; Bodrug S.; Kitada S.; Hanada M. (1996) BCL-2 family proteins: regulators of cell death involved in the pathogenesis of cancer and resistance to therapy. J. Cell. Biochem. 60, 23–32. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19960101)60:1<23::AID-JCB5>3.0.CO;2-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

