Association of Cold Ischemia Time With Acute Renal Transplant Rejection
- PMID: 29346257
- PMCID: PMC6023749
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002106
Association of Cold Ischemia Time With Acute Renal Transplant Rejection
Abstract
Background: Kidney transplantation holds much promise as a treatment of choice for patients with end-stage kidney disease. The impact of cold ischemia time (CIT) on acute renal transplant rejection (ARTR) remains to be fully studied in a large cohort of renal transplant patients.
Methods: From the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network database, we analyzed 63 798 deceased donor renal transplants performed between 2000 and 2010. We assessed the association between CIT and ARTR. We also evaluated the association between recipient age and ARTR.
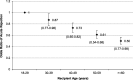
Results: Six thousand eight hundred two (11%) patients were clinically diagnosed with ARTR. Longer CIT was associated with an increased risk of ARTR. After multivariable adjustment, compared with recipients with CIT < 12 hours, the relative risk of ARTR was 1.13 (95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.23) in recipients with CIT ≥ 24 hours. The association of CIT and ARTR was more pronounced in patients undergoing retransplantation: compared with recipients with CIT less than 12 hours, the relative risk of ARTR was 1.66 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.73) in recipients with CIT of 24 hours or longer. Additionally, older age was associated with a decreased risk of ARTR. Compared with recipients aged 18 to 29 years, the relative risk of ARTR was 0.50 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.57) in recipients 60 years or older. Longer CIT was also associated with increased risk of death-censored graft loss. Compared with recipients with CIT less than 12 hours, the hazard ratio of death-censored graft loss was 1.22 (95% confidence interval, 1.14-1.30) in recipients with CIT of 24 hours or longer.
Conclusions: Prolonged CIT is associated with an increased risk of ARTR and death-censored graft loss. Older age was associated with a lower risk of ARTR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wolfe RA, Roys EC, Merion RM. Trends in organ donation and transplantation in the United States, 1999-2008 Am J Transplant 2010. 10961–972 - PubMed
-
- USRDS 2016. Annual Data Report. Volume 2: End-Stage Renal Disease in United States. 2016. https://www.usrds.org/2016/view/v2_07.aspx.
-
- Land WG. Injury to allografts: innate immune pathways to acute and chronic rejection Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 2005. 16520–539 - PubMed
-
- Alegre ML, Florquin S, Goldman M. Cellular mechanisms underlying acute graft rejection: time for reassessment Curr Opin Immunol 2007. 19563–568 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

