Chronic Dietary Intake of Enniatin B in Broiler Chickens Has Low Impact on Intestinal Morphometry and Hepatic Histology, and Shows Limited Transfer to Liver Tissue
- PMID: 29346316
- PMCID: PMC5793132
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10010045
Chronic Dietary Intake of Enniatin B in Broiler Chickens Has Low Impact on Intestinal Morphometry and Hepatic Histology, and Shows Limited Transfer to Liver Tissue
Abstract
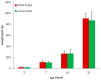
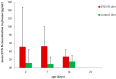
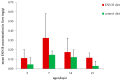
The Fusarium mycotoxin enniatin B (ENN B) is a so-called emerging mycotoxin frequently contaminating poultry feed. To investigate the impact of chronic ENN B exposure on animal health, broiler chickens were fed either a diet naturally contaminated with ENN B (2352 µg/kg) or a control diet (135 µg/kg) for 2, 7, 14, or 21 days. ENN B concentrations were determined in plasma and liver using a validated ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry UHPLC-MS/MS method. Liver was evaluated histologically, and the villus length and crypt depth of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum were measured. Histopathology of the livers did not reveal major abnormalities. Feeding an ENN B-contaminated diet could possibly inhibit the proliferation of enterocytes in the duodenal crypts, but did not affect villus length, crypt depth, or villus length-crypt depth ratio of the jejunum and ileum. ENN B levels in plasma and liver were significantly higher in the ENN B-fed group and ranged between <25-264 pg/mL and <0.05-0.85 ng/g, respectively. ENN B carry-over rates from feed to liver tissue were 0.005-0.014% and 0.034-0.109% in the ENN B and control group, respectively. Carry-over rates were low and indicated a limited contribution of poultry tissue-derived products to the total dietary ENN B intake for humans. The above results support the opinion of the European Food Safety Authority stating that adverse health effects from ENN B in broiler chickens are unlikely.
Keywords: Enniatin B; broiler chicken; carry-over; chronic dietary intake; intestinal toxicity; liver residue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Study of Carry-Over and Histopathological Effects after Chronic Dietary Intake of Citrinin in Pigs, Broiler Chickens and Laying Hens.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Nov 16;12(11):719. doi: 10.3390/toxins12110719. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33207646 Free PMC article.
-
Carry-over of some Fusarium mycotoxins in tissues and eggs of chickens fed experimentally mycotoxin-contaminated diets.Food Chem Toxicol. 2020 Nov;145:111715. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111715. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32871192
-
Effect of a Yeast β-Glucan on the Performance, Intestinal Integrity, and Liver Function of Broiler Chickens Fed a Diet Naturally Contaminated with Fusarium Mycotoxins.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jan 23;17(2):51. doi: 10.3390/toxins17020051. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39998068 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Mycotoxin Enniatin B.Front Public Health. 2017 Nov 16;5:304. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2017.00304. eCollection 2017. Front Public Health. 2017. PMID: 29201864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enniatin B1: Emerging Mycotoxin and Emerging Issues.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jun 6;15(6):383. doi: 10.3390/toxins15060383. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37368684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Untargeted Metabolomics Approach Correlated Enniatin B Mycotoxin Presence in Cereals with Kashin-Beck Disease Endemic Regions of China.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Aug 30;15(9):533. doi: 10.3390/toxins15090533. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755959 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Exposure to Multiple Mycotoxins: An Example of Using a Tiered Approach in a Mixture Risk Assessment.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Apr 26;14(5):303. doi: 10.3390/toxins14050303. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35622550 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Mycotoxin Occurrence in Dairy Cattle and Poultry Feeds and Feed Ingredients from Machakos Town, Kenya.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Dec 3;12(12):762. doi: 10.3390/toxins12120762. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33287105 Free PMC article.
-
Low Doses of Mycotoxin Mixtures below EU Regulatory Limits Can Negatively Affect the Performance of Broiler Chickens: A Longitudinal Study.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jul 1;12(7):433. doi: 10.3390/toxins12070433. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32630277 Free PMC article.
-
A Study of Carry-Over and Histopathological Effects after Chronic Dietary Intake of Citrinin in Pigs, Broiler Chickens and Laying Hens.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Nov 16;12(11):719. doi: 10.3390/toxins12110719. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33207646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Panel E.C. Scientific opinion on the risks to human and animal health related to the presence of beauvericin and enniatins in food and feed. EFSA J. 2014;12:3802.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

