Serious Fall Injury History and Adverse Health Outcomes After Initiating Hemodialysis Among Older U.S. Adults
- PMID: 29346522
- PMCID: PMC7190925
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glx260
Serious Fall Injury History and Adverse Health Outcomes After Initiating Hemodialysis Among Older U.S. Adults
Abstract
Background: Although older adults with predialysis chronic kidney disease are at higher risk for falls, the prognostic significance of a serious fall injury prior to dialysis initiation has not been well described in the end-stage renal disease population.
Methods: We examined the association between a serious fall injury in the year prior to starting hemodialysis and adverse health outcomes in the year following dialysis initiation using a retrospective cohort study of U.S. Medicare beneficiaries ≥ 67 years old who initiated dialysis in 2010-2012. Serious fall injuries were defined using diagnostic codes for falls plus an injury (fracture, joint dislocation, or head injury). Health outcomes, defined as time-to-event variables within the first year of dialysis, included four outcomes: a subsequent serious fall injury, hospital admission, post-acute skilled nursing facility (SNF) utilization, and mortality.
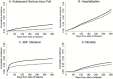
Results: Among this cohort of 81,653 initiating hemodialysis, 2,958 (3.6%) patients had a serious fall injury in the year prior to hemodialysis initiation. In the first year of dialysis, 7.6% had a subsequent serious fall injury, 67.6% a hospitalization, 30.7% a SNF claim, and 26.1% died. Those with versus without a serious fall injury in the year prior to hemodialysis initiation were at higher risk (hazard ratio, 95% confidence interval) for a subsequent serious fall injury (2.65, 2.41-2.91), hospitalization (1.11, 1.06-1.16), SNF claim (1.40, 1.30-1.50), and death (1.14, 1.06-1.22).
Conclusions: For older adults initiating dialysis, a history of a serious fall injury may provide prognostic information to support decision making and establish expectations for life after dialysis initiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serious Fall Injuries Before and After Initiation of Hemodialysis Among Older ESRD Patients in the United States: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2017 Jul;70(1):76-83. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.11.021. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017. PMID: 28139394
-
Association of Serious Fall Injuries among United States End Stage Kidney Disease Patients with Access to Kidney Transplantation.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Apr 6;13(4):628-637. doi: 10.2215/CJN.10330917. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29511059 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Nondisease-Specific Problems with Mortality, Long-Term Care, and Functional Impairment among Older Adults Who Require Skilled Nursing Care after Dialysis Initiation.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Dec 7;11(12):2218-2224. doi: 10.2215/CJN.01260216. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27733436 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Reduced eGFR and Albuminuria with Serious Fall Injuries among Older Adults.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Jul 7;11(7):1236-1243. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11111015. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27091516 Free PMC article.
-
Falls in elderly hemodialysis patients.QJM. 2011 Oct;104(10):829-38. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcr108. Epub 2011 Jul 12. QJM. 2011. PMID: 21750022 Review.
Cited by
-
Walking aids and complicated orthopedic diseases are risk factors for falls in hemodialysis patients: an observational study.BMC Geriatr. 2023 May 22;23(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-04015-9. BMC Geriatr. 2023. PMID: 37217875 Free PMC article.
-
Dialysis or kidney transplantation in older adults? A systematic review summarizing functional, psychological, and quality of life-related outcomes after start of kidney replacement therapy.Int Urol Nephrol. 2022 Nov;54(11):2891-2900. doi: 10.1007/s11255-022-03208-2. Epub 2022 May 6. Int Urol Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35513758 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for mortality in elderly haemodialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Aug 31;21(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-02026-x. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32867718 Free PMC article.
-
Higher Amounts of Opioids Filled After Surgery Increase Risk of Serious Falls and Fall-Related Injuries Among Older Adults.J Gen Intern Med. 2020 Oct;35(10):2917-2924. doi: 10.1007/s11606-020-06015-6. Epub 2020 Aug 3. J Gen Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32748343 Free PMC article.
-
Mobility Impairment in Patients New to Dialysis.Am J Nephrol. 2020;51(9):705-714. doi: 10.1159/000509225. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Am J Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32781443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tinetti ME, Williams CS. Falls, injuries due to falls, and the risk of admission to a nursing home. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1279–1284. doi:10.1056/NEJM199710303371806 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

