Efficacy of Empirical Therapy With Combined Ciprofloxacin Versus Topical Drops Alone in Patients With Tubotympanic Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial
- PMID: 29348711
- PMCID: PMC5768256
- DOI: 10.1177/1179550617751907
Efficacy of Empirical Therapy With Combined Ciprofloxacin Versus Topical Drops Alone in Patients With Tubotympanic Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: One of the prevailing otologic infections in our country is chronic suppurative otitis media, especially the tubotympanic type for which various treatment protocols are followed. Usually, oral and topical antibiotics (mainly quinolones) are given alone or in combination. There is a lack of consensus as to whether topical drops alone are effective or a combined oral and systemic therapy should be prescribed. In our study, we have attempted to observe the efficacy of empirical therapy with combined ciprofloxacin versus topical drops only in patients with tubotympanic chronic suppurative otitis media for control of infection.
Methodology: A total of 100 patients visiting the outpatient ENT department at our tertiary care hospital with clinically diagnosed chronic suppurative otitis media (tubotympanic type) were enrolled in our study. The study was reviewed and accepted by the ethical review committee. A detailed proforma was filled for all patients. All patients after aural toilet were subjected randomly to one of the 2 treatment methods, ie, topical ciprofloxacin ear drops plus an oral placebo or combined oral and topical ciprofloxacin. These patients were reviewed after 1 week of treatment.
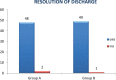
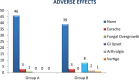
Results: It was observed that 48 of 50 (96%) patients responded to treatment in the group receiving topical ciprofloxacin, whereas 49 of 50 (98%) patients responded in the group receiving combined therapy. This difference was not significant. Moreover, age, sex, and duration of discharge did not have any effect on treatment. There were minimal side effects in both groups, which were also not significant and disappeared after discontinuation of treatment.
Conclusions: The results of this study show that topical ciprofloxacin drops were as effective as combined oral and topical ciprofloxacin and that the addition of oral drug did not have any beneficial effect and added only to the cost of treatment.
Keywords: Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM); Pseudomonas aeruginosa; empirical antibiotics; otorrhea.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests:The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Verhoeff M, van der Veen EL, Rovers MM, Sanders EA, Schilder AG. Chronic suppurative otitis media: a review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006;70:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Gleeson M, Browning GG, Burton MJ, et al. Scott-Brown’s Otolaryngology, Otology. 7th ed. Vol. 2 Oxford, UK: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2004.
-
- World Health Organization. Prevention of hearing impairment from chronic otitis media: report of a WHO/CIBA Foundation workshop. Paper presented at: Prevention of hearing impairment from chronic otitis media: report of a WHO/CIBA Foundation Workshop; November 19-21, 1996; London, UK.
-
- Aslam MA, Ahmed Z, Azim R. Microbiology and drug sensitivity patterns of chronic suppurative otitis media. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2004;14:459–461. - PubMed
-
- Iqbal S, Udaipurwala IH, Hasan A, Shafiq M, Mughal S. Chronic suppurative otitis media: disease pattern and drug sensitivity. J Surg Pak. 2006;11:17–19.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous