Preparation of P3HB4HB/(Gelatin + PVA) Composite Scaffolds by Coaxial Electrospinning and Its Biocompatibility Evaluation
- PMID: 29349086
- PMCID: PMC5733976
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9251806
Preparation of P3HB4HB/(Gelatin + PVA) Composite Scaffolds by Coaxial Electrospinning and Its Biocompatibility Evaluation
Abstract
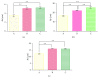
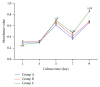
This study was conducted to prepare coaxial electrospun scaffolds of P3HB4HB/(gelatin + PVA) with various concentration ratios with P3HB4HB as the core solution and gelatin + PVA mixture as the shell solution; the mass ratios of gelatin and PVA in each 10 mL shell mixture were 0.6 g : 0.2 g (Group A), 0.4 g : 0.4 g (Group B), and 0.2 g : 0.6 g (Group C). The results showed that the pore size, porosity, and cell proliferation rate of Group C were better than those of Groups A and B. The ascending order of the tensile strength and modulus of elasticity was Group A < Group B < Group C. The surface roughness was Group C > Group B > Group A. The osteogenic and chondrogenic-specific staining showed that Group C was stronger than Groups A and B. This study demonstrates that when the mass ratio of gelatin : PVA was 0.2 g : 0.6 g, a P3HB4HB/(gelatin + PVA) composite scaffold with a core-shell structure can be prepared, and the scaffold has good biocompatibility that it may be an ideal scaffold for tissue engineering.
Figures









References
-
- Chang H. C., Sun T., Sultana N., Lim M. M., Khan T. H., Ismail A. F. Conductive PEDOT : PSS coated polylactide (PLA) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) electrospun membranes: fabrication and characterization. Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2016;61:396–410. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.12.074. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thien D. V. H., Hsiao S. W., Ho M. H., Li C. H., Shih J. L. Electrospun chitosan/hydroxyapatite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. Journal of Materials Science. 2013;48(4):1640–1645. doi: 10.1007/s10853-012-6921-1. - DOI
-
- McClure M. J., Wolfe P. S., Rodriguez I. A., Bowlin G. L. Bioengineered vascular grafts: Improving vascular tissue engineering through scaffold design. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology. 2011;21(3):211–227. doi: 10.1016/S1773-2247(11)50030-9. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

