Comparing methods of targeting obesity interventions in populations: An agent-based simulation
- PMID: 29349218
- PMCID: PMC5769018
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ssmph.2017.01.006
Comparing methods of targeting obesity interventions in populations: An agent-based simulation
Abstract
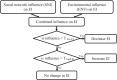
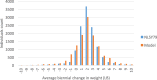
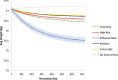
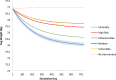
Social networks as well as neighborhood environments have been shown to effect obesity-related behaviors including energy intake and physical activity. Accordingly, harnessing social networks to improve targeting of obesity interventions may be promising to the extent this leads to social multiplier effects and wider diffusion of intervention impact on populations. However, the literature evaluating network-based interventions has been inconsistent. Computational methods like agent-based models (ABM) provide researchers with tools to experiment in a simulated environment. We develop an ABM to compare conventional targeting methods (random selection, based on individual obesity risk, and vulnerable areas) with network-based targeting methods. We adapt a previously published and validated model of network diffusion of obesity-related behavior. We then build social networks among agents using a more realistic approach. We calibrate our model first against national-level data. Our results show that network-based targeting may lead to greater population impact. We also present a new targeting method that outperforms other methods in terms of intervention effectiveness at the population level.
Keywords: Agent-based modeling; Effectiveness; Influence maximization; Intervention targeting; Obesity; Simulation; Social networks.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Influence of a School Social Network Intervention on Adolescent's Health Behaviors: A Gender-Specific Agent-Based Model.Front Public Health. 2022 Apr 4;10:861743. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.861743. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35444977 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Influence Agents That Promote Physical Activity Through the Simulation of Social Network Interventions: Agent-Based Modeling Study.J Med Internet Res. 2019 Aug 5;21(8):e12914. doi: 10.2196/12914. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31381504 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating social network-based weight loss interventions in Chinese population: An agent-based simulation.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 3;15(8):e0236716. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236716. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32745125 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of social network analysis to obesity: a systematic review.Obes Rev. 2018 Jul;19(7):976-988. doi: 10.1111/obr.12684. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Obes Rev. 2018. PMID: 29676508
-
A narrative review of the use of agent-based modeling in health behavior and behavior intervention.Transl Behav Med. 2019 Nov 25;9(6):1065-1075. doi: 10.1093/tbm/iby132. Transl Behav Med. 2019. PMID: 30649559 Review.
Cited by
-
Concurrent Imputation and Prediction on EHR data using Bi-Directional GANs: Bi-GANs for EHR imputation and prediction.ACM BCB. 2021 Aug;2021:7. doi: 10.1145/3459930.3469512. ACM BCB. 2021. PMID: 34604866 Free PMC article.
-
A predictive model of rat calorie intake as a function of diet energy density.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018 Aug 1;315(2):R256-R266. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00337.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29341825 Free PMC article.
-
A scoping review of systems approaches for increasing physical activity in populations.Health Res Policy Syst. 2022 Sep 29;20(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12961-022-00906-2. Health Res Policy Syst. 2022. PMID: 36175916 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing targeting strategies for network-based adolescent drinking interventions: A simulation approach.Soc Sci Med. 2021 Aug;282:114136. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.114136. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Soc Sci Med. 2021. PMID: 34175574 Free PMC article.
-
The Usefulness of Web-Based Communication Data for Social Network Health Interventions: Agent-Based Modeling Study.JMIR Pediatr Parent. 2023 Nov 22;6:e44849. doi: 10.2196/44849. JMIR Pediatr Parent. 2023. PMID: 37991813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali M.M., Amialchuk A., Gao S., Heiland F. Adolescent weight gain and social networks: Is there a contagion effect? Applied Economics. 2012;44:2969–2983.
-
- Ali M.M., Amialchuk A., Rizzo J.A. The influence of body weight on social network ties among adolescents. Economics and Human Biology. 2012;10:20–34. - PubMed
-
- Altarelli F., Braunstein A., Dall’Asta L., Wakeling J.R., Zecchina R. Containing epidemic outbreaks by message-passing techniques. Physical Review X. 2014;4:021024.
-
- Auchincloss A.H., Diez Roux A.V. A new tool for epidemiology: The usefulness of dynamic-agent models in understanding place effects on health. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2008;168:1–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

