Case-Based Learning and its Application in Medical and Health-Care Fields: A Review of Worldwide Literature
- PMID: 29349306
- PMCID: PMC5736264
- DOI: 10.4137/JMECD.S20377
Case-Based Learning and its Application in Medical and Health-Care Fields: A Review of Worldwide Literature
Abstract
Introduction: Case-based learning (CBL) is a newer modality of teaching healthcare. In order to evaluate how CBL is currently used, a literature search and review was completed.
Methods: A literature search was completed using an OVID© database using PubMed as the data source, 1946-8/1/2015. Key words used were "Case-based learning" and "medical education", and 360 articles were retrieved. Of these, 70 articles were selected to review for location, human health care related fields of study, number of students, topics, delivery methods, and student level.
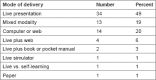
Results: All major continents had studies on CBL. Education levels were 64% undergraduate and 34% graduate. Medicine was the most frequently represented field, with articles on nursing, occupational therapy, allied health, child development and dentistry. Mean number of students per study was 214 (7-3105). The top 3 most common methods of delivery were live presentation in 49%, followed by computer or web-based in 20% followed by mixed modalities in 19%. The top 3 outcome evaluations were: survey of participants, knowledge test, and test plus survey, with practice outcomes less frequent. Selected studies were reviewed in greater detail, highlighting advantages and disadvantages of CBL, comparisons to Problem-based learning, variety of fields in healthcare, variety in student experience, curriculum implementation, and finally impact on patient care.
Conclusions: CBL is a teaching tool used in a variety of medical fields using human cases to impart relevance and aid in connecting theory to practice. The impact of CBL can reach from simple knowledge gains to changing patient care outcomes.
Keywords: case-based learning; graduate medical education; medical curriculum; medical education.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests:Author discloses no external Funding sources.
Figures
References
-
- Knowles M.S., Holton E.F., Swanson R.A. The Adult Learner: The Definitive Classic in Adult Education and Human Resource Development. St. Louis: Elsevier; 2005.
-
- Eisenstein A., Vaisman L., Johnston-Cox H. et al. Integration of basic science and clinical medicine: the innovative approach of the cadaver biopsy project at the Boston University School of Medicine. Acad Med. 2014; 89(1): 50–52. - PubMed
-
- Thistlewaite J.E., Davies D., Ekeocha S. et al. The effectiveness of case based learning in health professional education. A BEME systematic review. BEME guide number 23. Med Teach. 2012; 34: E421–E444. - PubMed
-
- Srinivasan M., Wilkes M., Stevenson F., Nguyen T., Slavin S. Comparing problem-based learning with case-based learning: effects of a major curricular shift at two institutions. Acad Med. 2007; 82(1): 74–82. - PubMed
-
- Frengley R.W., Weller J.M., Torrie J. et al. The effect of a simulation-based intervention on the performance of established critical care unit team. Crit Care Med. 2011; 39(12): 2605–2611. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous