The Adverse Effects of Environmental Noise Exposure on Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Risk
- PMID: 29350061
- PMCID: PMC5898791
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2017.7118
The Adverse Effects of Environmental Noise Exposure on Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Risk
Abstract
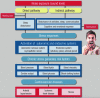
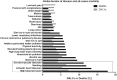
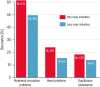
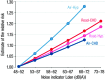
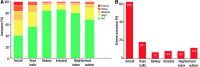
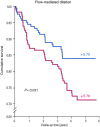
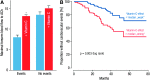
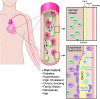
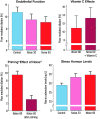
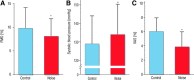
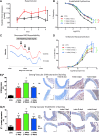
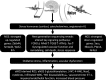
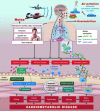
Epidemiological studies have provided evidence that traffic noise exposure is linked to cardiovascular diseases such as arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction, and stroke. Noise is a nonspecific stressor that activates the autonomous nervous system and endocrine signaling. According to the noise reaction model introduced by Babisch and colleagues, chronic low levels of noise can cause so-called nonauditory effects, such as disturbances of activity, sleep, and communication, which can trigger a number of emotional responses, including annoyance and subsequent stress. Chronic stress in turn is associated with cardiovascular risk factors, comprising increased blood pressure and dyslipidemia, increased blood viscosity and blood glucose, and activation of blood clotting factors, in animal models and humans. Persistent chronic noise exposure increases the risk of cardiometabolic diseases, including arterial hypertension, coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus type 2, and stroke. Recently, we demonstrated that aircraft noise exposure during nighttime can induce endothelial dysfunction in healthy subjects and is even more pronounced in coronary artery disease patients. Importantly, impaired endothelial function was ameliorated by acute oral treatment with the antioxidant vitamin C, suggesting that excessive production of reactive oxygen species contributes to this phenomenon. More recently, we introduced a novel animal model of aircraft noise exposure characterizing the underlying molecular mechanisms leading to noise-dependent adverse oxidative stress-related effects on the vasculature. With the present review, we want to provide an overview of epidemiological, translational clinical, and preclinical noise research addressing the nonauditory, adverse effects of noise exposure with focus on oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 28, 873-908.
Keywords: aircraft noise exposure; endothelial dysfunction; environmental risk factors; oxidative stress; stress hormones; traffic noise exposure.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Environmental noise induces the release of stress hormones and inflammatory signaling molecules leading to oxidative stress and vascular dysfunction-Signatures of the internal exposome.Biofactors. 2019 Jul;45(4):495-506. doi: 10.1002/biof.1506. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Biofactors. 2019. PMID: 30937979 Review.
-
Cardiovascular effects of environmental noise exposure.Eur Heart J. 2014 Apr;35(13):829-36. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu030. Epub 2014 Mar 9. Eur Heart J. 2014. PMID: 24616334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental Noise and the Cardiovascular System.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Feb 13;71(6):688-697. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.12.015. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29420965 Review.
-
Too Loud to Handle? Transportation Noise and Cardiovascular Disease.Can J Cardiol. 2023 Sep;39(9):1204-1218. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2023.02.018. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Can J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36858080 Review.
-
Ecology of the cardiovascular system: Part II - A focus on non-air related pollutants.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2019 Jul;29(5):274-282. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Sep 8. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2019. PMID: 30224235 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of aircraft noise on vascular and cardiac function in relation to noise event number: a randomized trial.Cardiovasc Res. 2021 Apr 23;117(5):1382-1390. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa204. Cardiovasc Res. 2021. PMID: 32914847 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Road Traffic Noise Exposure and Filled Prescriptions for Antihypertensive Medication: A Danish Cohort Study.Environ Health Perspect. 2020 May;128(5):57004. doi: 10.1289/EHP6273. Epub 2020 May 14. Environ Health Perspect. 2020. PMID: 32438890 Free PMC article.
-
Noise annoyance and cardiovascular disease risk: results from a 10-year follow-up study.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 7;14(1):5619. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56250-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38454061 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress in the brain is regulated by social status in a highly social cichlid fish.Front Behav Neurosci. 2024 Nov 26;18:1477984. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2024.1477984. eCollection 2024. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39659705 Free PMC article.
-
Transportation noise pollution and cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021 Sep;18(9):619-636. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00532-5. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33790462 Review.
References
-
- Spiegel Online. 1968. www.spiegel.de/spiegel/print/d-46106751.html (accessed February9, 2018)
-
- WHO and JRC Report. Burden of disease from environmental noise. 20113. www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0008/136466/e94888.pdf (accessed February9, 2018)
-
- ENNAH—European Network on Noise and Health. 2013. http://www.ennah.eu/home?lang=en (accessed February9, 2018)
-
- Noise in Europe 2014. EEA Report 10. 2014. www.eea.europa.eu/publications/noise-in-europe-2014 (accessed February9, 2018)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
