Use of Pristinamycin for Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma genitalium Infection
- PMID: 29350154
- PMCID: PMC5782881
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2402.170902
Use of Pristinamycin for Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma genitalium Infection
Abstract
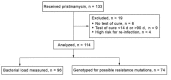
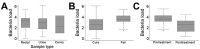
High levels of macrolide resistance and increasing fluoroquinolone resistance are found in Mycoplasma genitalium in many countries. We evaluated pristinamycin for macrolide-resistant M. genitalium in a sexual health center in Australia. Microbiologic cure was determined by M. genitalium-specific 16S PCR 14-90 days after treatment began. Of 114 persons treated with pristinamycin, infection was cured in 85 (75%). This percentage did not change when pristinamycin was given at daily doses of 2 g or 4 g or at 3 g combined with 200 mg doxycycline. In infections with higher pretreatment bacterial load, treatment was twice as likely to fail for each 1 log10 increase in bacterial load. Gastrointestinal side effects occurred in 7% of patients. Pristinamycin at maximum oral dose, or combined with doxycycline, cured 75% of macrolide-resistant M. genitalium infections. Pristinamycin is well-tolerated and remains an option where fluoroquinolones have failed or cannot be used.
Keywords: Australia; Mycoplasma genitalium; antimicrobal resistance; bacteria; nongonococcal urethritis; pelvic inflammatory disease; pristinamycin; sexually transmitted infections.
Figures
References
-
- Antbiotic Expert Groups, editor. Genital and sexually transmitted infections. In: Therapeutic guidelines: antibiotic. 15th ed. Melbourne (Australia): Therapeutic Guidelines Limited; 2014. p. 439–67.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

