Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma
- PMID: 29350646
- PMCID: PMC6179079
- DOI: 10.23750/abm.v89i1-S.7021
Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma
Abstract
Osteoid osteoma is a benign bone neoplasm with a reported incidence of 2-3% among all bone primary tumors. Although it is a small and benign lesion, it is often cause of patient complaint and discomfort. It is generally characterized by a long lasting, unremitting pain that typically exacerbates at night, often leading to sleep deprivation and functional limitation of the skeletal segment involved, with a significant reduction of patient daily life activities and consequent worsening of the overall quality of life. Over decades, complete surgical resection has represented the only curative treatment for symptomatic patients. In the last years, new percutaneous ablation techniques, especially radiofrequency ablation, have been reported to be a safe and effective alternative to classical surgery, with a low complication and recurrence rate, and a significant reduction in hospitalization cost and duration. The aim of this article is to provide an overview about the radiofrequency thermal ablation procedure in the treatment of osteoid osteoma.
Keywords: Interventional radiology, Osteoid Osteoma, Bone tumors, Radiofrequency ablation.
Figures
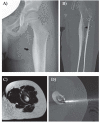
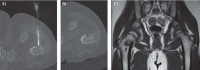

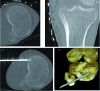
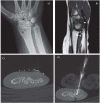
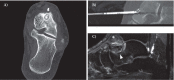
References
-
- Torg JS, Loughran T, Pavlov H, Schwamm H, Gregg J, Sherman M, Balduini FC. Osteoid osteoma. Distant, periarticular, and subarticular lesions as a cause of knee pain. Sports Med. 1985;2:296–304. - PubMed
-
- Izzo R, Guarnieri G, Guglielmi G, Muto M. Biomechanics of the spine. Part I: Spinal stability. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:118–126. - PubMed
-
- Masala S, Nano G, Marcia S, Muto M, Fucci FPM, Simonetti G. Osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture augmentation by injectable partly resorbable ceramic bone substitute (Cerament™|SPINESUPPORT): A prospective nonrandomized study. Neuroradiology. 2012;54:1245–1251. - PubMed
-
- Guarnieri G, Vassallo P, Pezzullo MG, Laghi F, Zeccolini F, Ambrosanio G, Galasso R, Muto M, Izzo R. A comparison of minimally invasive techniques in percutaneous treatment of lumbar herniated discs a review. Neuroradiol J. 2009;22:108–121. - PubMed
-
- Cellerini M, Mangiafico S, Ammannati F, Ambrosanio G, Muto M, Galasso L, Mennonna P. Ruptured, dissecting posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms: Endovascular treatment without parent vessel occlusion. Neuroradiology. 2008;50:315–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

