Physiology of Astroglia
- PMID: 29351512
- PMCID: PMC6050349
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00042.2016
Physiology of Astroglia
Abstract
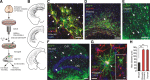
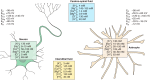
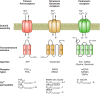
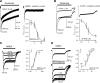
Astrocytes are neural cells of ectodermal, neuroepithelial origin that provide for homeostasis and defense of the central nervous system (CNS). Astrocytes are highly heterogeneous in morphological appearance; they express a multitude of receptors, channels, and membrane transporters. This complement underlies their remarkable adaptive plasticity that defines the functional maintenance of the CNS in development and aging. Astrocytes are tightly integrated into neural networks and act within the context of neural tissue; astrocytes control homeostasis of the CNS at all levels of organization from molecular to the whole organ.
Figures






















References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Boeynaems JM, Barnard EA, Boyer JL, Kennedy C, Knight GE, Fumagalli M, Gachet C, Jacobson KA, Weisman GA. International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol Rev 58: 281–341, 2006. doi: 10.1124/pr.58.3.3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

