Sex and Race Differences in Lifetime Risk of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction and Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction
- PMID: 29352072
- PMCID: PMC6417883
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031622
Sex and Race Differences in Lifetime Risk of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction and Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction
Abstract
Background: Lifetime risk of heart failure has been estimated to range from 20% to 46% in diverse sex and race groups. However, lifetime risk estimates for the 2 HF phenotypes, HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), are not known.
Methods: Participant-level data from 2 large prospective cohort studies, the CHS (Cardiovascular Health Study) and MESA (Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis), were pooled, excluding individuals with prevalent HF at baseline. Remaining lifetime risk estimates for HFpEF (EF ≥45%) and HFrEF (EF <45%) were determined at different index ages with the use of a modified Kaplan-Meier method with mortality and the other HF subtype as competing risks.
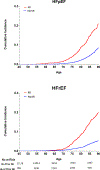
Results: We included 12 417 participants >45 years of age (22.2% blacks, 44.8% men) who were followed up for median duration of 11.6 years with 2178 overall incident HF events with 561 HFrEF events and 726 HFpEF events. At the index age of 45 years, the lifetime risk for any HF through 90 years of age was higher in men than women (27.4% versus 23.8%). Among HF subtypes, the lifetime risk for HFrEF was higher in men than women (10.6% versus 5.8%). In contrast, the lifetime risk for HFpEF was similar in men and women. In race-stratified analyses, lifetime risk for overall HF was higher in nonblacks than blacks (25.9% versus 22.4%). Among HF subtypes, the lifetime risk for HFpEF was higher in nonblacks than blacks (11.2% versus 7.7%), whereas that for HFrEF was similar across the 2 groups. Among participants with antecedent myocardial infarction before HF diagnosis, the remaining lifetime risks for HFpEF and HFrEF were up to 2.5-fold and 4-fold higher, respectively, compared with those without antecedent myocardial infarction.
Conclusions: Lifetime risks for HFpEF and HFrEF vary by sex, race, and history of antecedent myocardial infarction. These insights into the distribution of HF risk and its subtypes could inform the development of targeted strategies to improve population-level HF prevention and control.
Keywords: heart failure; risk.
© 2018 American Heart Association, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Das SR, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Floyd J, Fornage M, Gillespie C, Isasi CR, Jimenez MC, Jordan LC, Judd SE, Lackland D, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth L, Liu S, Longenecker CT, Mackey RH, Matsushita K, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Thiagarajan RR, Reeves MJ, Ritchey M, Rodriguez CJ, Roth GA, Rosamond WD, Sasson C, Towfighi A, Tsao CW, Turner MB, Virani SS, Voeks JH, Willey JZ, Wilkins JT, Wu JH, Alger HM, Wong SS, Muntner P, American Heart Association Statistics C and Stroke Statistics S. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135:e146–e603. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr., Drazner MH, Fonarow GC, Geraci SA, Horwich T, Januzzi JL, Johnson MR, Kasper EK, Levy WC, Masoudi FA, McBride PE, McMurray JJ, Mitchell JE, Peterson PN, Riegel B, Sam F, Stevenson LW, Tang WH, Tsai EJ and Wilkoff BL. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128:1810–52. - PubMed
-
- Dunlay SM, Roger VL and Redfield MM. Epidemiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017;14(10):591–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

