Incident Heart Failure in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- PMID: 29352092
- PMCID: PMC5850154
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007227
Incident Heart Failure in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease associated with a wide range of comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, but its association with heart failure (HF) is not fully clear. We investigated the risk of incident HF in a nationwide cohort of patients with RA.
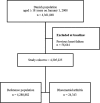
Methods and results: The study comprised the entire Danish population aged ≥18 years followed from January 1, 2008 until first hospitalization for HF, emigration, December 31, 2012, or death. Information on comorbidity, medication, and socioeconomic status was identified by individual-level linkage of administrative registers. Patients with a rheumatologist diagnosis of RA between 1978 and 2008 were included. The primary study outcome was incident HF defined as first hospital admission for HF. Incidence rates of HF per 1000 person-years were calculated and incidence rate ratios adjusted for age, sex, calendar year, comorbidity, medications, socioeconomic status, smoking, and alcohol consumption were estimated. A total of 4 305 225 subjects with no history of HF were eligible for analysis at the study start. Of these subjects, 24 343 developed RA and 50 623 were hospitalized for HF. Overall incidence rates of incident HF were 2.43 and 6.64 for the reference population (n=49 879) and patients with RA (n=744), respectively. Correspondingly, the fully adjusted incidence rate ratio for incident HF was increased in patients with RA with incidence rate ratio 1.30 (95% confidence interval, 1.17-1.45).
Conclusions: In this cohort study, RA was associated with an increased hospitalization for HF. These findings add significantly to the existing evidence of RA as a clinically relevant risk factor for HF.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; heart failure; inflammation; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2018 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures
References
-
- Armstrong EJ, Harskamp CT, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis and major adverse cardiovascular events: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of observational studies. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2:e000062 DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000062. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avina‐Zubieta JA, Thomas J, Sadatsafavi M, Lehman AJ, Lacaille D. Risk of incident cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta‐analysis of observational studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:1524–1529. - PubMed
-
- Soubrier M, Barber Chamoux N, Tatar Z, Couderc M, Dubost JJ, Mathieu S. Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2014;81:298–302. - PubMed
-
- Ahlehoff O, Gislason GH, Charlot M, Jorgensen CH, Lindhardsen J, Olesen JB, Abildstrøm SZ, Skov L, Torp‐Pedersen C, Hansen PR. Psoriasis is associated with clinically significant cardiovascular risk: a Danish nationwide cohort study. J Intern Med. 2011;270:147–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous