An ornithine ω-aminotransferase required for growth in the absence of exogenous proline in the archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis
- PMID: 29352105
- PMCID: PMC5846162
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001222
An ornithine ω-aminotransferase required for growth in the absence of exogenous proline in the archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis
Abstract
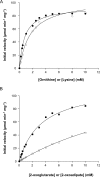
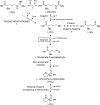
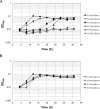
Aminotransferases are pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent enzymes that catalyze reversible transamination reactions between amino acids and α-keto acids, and are important for the cellular metabolism of nitrogen. Many bacterial and eukaryotic ω-aminotransferases that use l-ornithine (Orn), l-lysine (Lys), or γ-aminobutyrate (GABA) have been identified and characterized, but the corresponding enzymes from archaea are unknown. Here, we examined the activity and function of TK2101, a gene annotated as a GABA aminotransferase, from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis We overexpressed the TK2101 gene in T. kodakarensis and purified and characterized the recombinant protein and found that it displays only low levels of GABA aminotransferase activity. Instead, we observed a relatively high ω-aminotransferase activity with l-Orn and l-Lys as amino donors. The most preferred amino acceptor was 2-oxoglutarate. To examine the physiological role of TK2101, we created a TK2101 gene-disruption strain (ΔTK2101), which was auxotrophic for proline. Growth comparison with the parent strain KU216 and the biochemical characteristics of the protein strongly suggested that TK2101 encodes an Orn aminotransferase involved in the biosynthesis of l-Pro. Phylogenetic comparisons of the TK2101 sequence with related sequences retrieved from the databases revealed the presence of several distinct protein groups, some of which having no experimentally studied member. We conclude that TK2101 is part of a novel group of Orn aminotransferases that are widely distributed at least in the genus Thermococcus, but perhaps also throughout the Archaea.
Keywords: amino acid; aminotransferase; archaea; biosynthesis; enzyme; metabolism; ornithine; proline; thermophile; transamination.
© 2018 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures




Similar articles
-
TK2268 encodes the major aminotransferase involved in the conversion from oxaloacetic acid to aspartic acid in Thermococcus kodakarensis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Mar 19;91(3):e0201724. doi: 10.1128/aem.02017-24. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39992121 Free PMC article.
-
TK1211 Encodes an Amino Acid Racemase towards Leucine and Methionine in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis.J Bacteriol. 2021 Mar 8;203(7):e00617-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00617-20. Print 2021 Mar 8. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 33468590 Free PMC article.
-
The TK0271 Protein Activates Transcription of Aromatic Amino Acid Biosynthesis Genes in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis.mBio. 2019 Sep 10;10(5):e01213-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01213-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31506306 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of 25 years of research on Thermococcus kodakarensis, a genetically versatile model organism for archaeal research.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2020 Feb;65(1):67-78. doi: 10.1007/s12223-019-00730-2. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2020. PMID: 31286382 Review.
-
Ornithine aminotransferase versus GABA aminotransferase: implications for the design of new anticancer drugs.Med Res Rev. 2015 Mar;35(2):286-305. doi: 10.1002/med.21328. Epub 2014 Aug 22. Med Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 25145640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heterologous gene expression and characterization of two serine hydroxymethyltransferases from Thermoplasma acidophilum.Extremophiles. 2021 Jul;25(4):393-402. doi: 10.1007/s00792-021-01238-9. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Extremophiles. 2021. PMID: 34196829
-
A Structurally Novel Lipoyl Synthase in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Nov 10;86(23):e01359-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01359-20. Print 2020 Nov 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32978128 Free PMC article.
-
TK2268 encodes the major aminotransferase involved in the conversion from oxaloacetic acid to aspartic acid in Thermococcus kodakarensis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Mar 19;91(3):e0201724. doi: 10.1128/aem.02017-24. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39992121 Free PMC article.
-
TK1211 Encodes an Amino Acid Racemase towards Leucine and Methionine in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis.J Bacteriol. 2021 Mar 8;203(7):e00617-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00617-20. Print 2021 Mar 8. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 33468590 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and genetic examination of two aminotransferases from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis.Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 20;14:1126218. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1126218. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36891395 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marino G., Nitti G., Arnone M. I., Sannia G., Gambacorta A., and De Rosa M. (1988) Purification and characterization of aspartate aminotransferase from the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 12305–12309 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

