Hyper-hippocampal glycogen induced by glycogen loading with exhaustive exercise
- PMID: 29352196
- PMCID: PMC5775355
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-19445-4
Hyper-hippocampal glycogen induced by glycogen loading with exhaustive exercise
Abstract
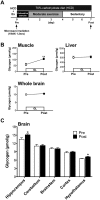
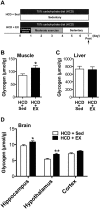
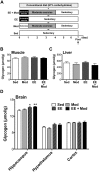
Glycogen loading (GL), a well-known type of sports conditioning, in combination with exercise and a high carbohydrate diet (HCD) for 1 week enhances individual endurance capacity through muscle glycogen supercompensation. This exercise-diet combination is necessary for successful GL. Glycogen in the brain contributes to hippocampus-related memory functions and endurance capacity. Although the effect of HCD on the brain remains unknown, brain supercompensation occurs following exhaustive exercise (EE), a component of GL. We thus employed a rat model of GL and examined whether GL increases glycogen levels in the brain as well as in muscle, and found that GL increased glycogen levels in the hippocampus and hypothalamus, as well as in muscle. We further explored the essential components of GL (exercise and/or diet conditions) to establish a minimal model of GL focusing on the brain. Exercise, rather than a HCD, was found to be crucial for GL-induced hyper-glycogen in muscle, the hippocampus and the hypothalamus. Moreover, EE was essential for hyper-glycogen only in the hippocampus even without HCD. Here we propose the EE component of GL without HCD as a condition that enhances brain glycogen stores especially in the hippocampus, implicating a physiological strategy to enhance hippocampal functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ahlborg B, Bergstrom J, Ekelund L, Hultman E. Muscle glycogen and msucle electrolytes during prolonged phyiscal exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1967;70:129–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03608.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

