Process Safety Assessment of the Iron-Catalyzed Direct Olefin Diazidation for the Expedient Synthesis of Vicinal Primary Diamines
- PMID: 29353989
- PMCID: PMC5773106
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.oprd.7b00312
Process Safety Assessment of the Iron-Catalyzed Direct Olefin Diazidation for the Expedient Synthesis of Vicinal Primary Diamines
Abstract
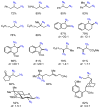
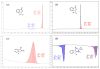
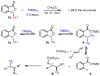
We report herein a process safety assessment of the iron-catalyzed direct olefin diazidation for the preparation of a broad range of synthetically valuable vicinal primary diamines. Differential scanning calorimetry analysis of the corresponding reagents, intermediates, and a list of representative diazide/diaminium salt products revealed that all of them are thermal stable at the reaction temperature. The drop weight test of the diazides suggested that they are moderately impact-sensitive. Guided by this assessment, an optimized olefin diazidation/diamination procedure has been developed which allows for the gram-scale diaminium salt synthesis without purification of the diazide intermediate.
Conflict of interest statement
Notes The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
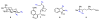


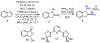

References
-
-
For selected references of olefin diamination reactions, see: Chong AO, Oshima K, Sharpless KB. J Am Chem Soc. 1977;99:3420.Bäckvall JE. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978;19:163.Becker PN, White MA, Bergman RG. J Am Chem Soc. 1980;102:5676.Li G, Wei HX, Kim SH, Carducci MD. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2001;40:4277.Bar GLJ, Lloyd-Jones GC, Booker-Milburn KI. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:7308.Streuff J, Hövelmann CH, Nieger M, Muñiz K. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:14586.Zabawa TP, Kasi D, Chemler SR. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:11250.Du H, Yuan W, Zhao B, Shi Y. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:11688.Zhao BG, Peng XG, Cui SL, Shi YA. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:11009.Zhao B, Peng X, Zhu Y, Ramirez TA, Cornwall RG, Shi Y. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:20890.Sibbald PA, Rosewall CF, Swartz RD, Michael FE. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:15945.Iglesias Á, Pérez EG, Muñiz K. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2010;49:8109.Olson DE, Su JY, Roberts DA, Du Bois J. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:13506.
-
-
-
For selected references of enantioselective olefin diamination reactions, see ref , and Du H, Zhao B, Yuan W, Shi Y. Org Lett. 2008;10:4231.Huang DS, Wang HN, Xue FZ, Guan H, Li LJ, Peng XY, Shi Y. Org Lett. 2011;13:6350.Röben C, Souto JA, González Y, Lishchynskyi A, Muñiz K. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2011;50:9478.Muñiz K, Barreiro L, Romero RM, Martínez C. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139:4354.Ingalls EL, Sibbald PA, Kaminsky W, Michael FE. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:8854.
-
-
-
For selected examples of chemical olefin diazidation methods, see: Minisci F. Acc Chem Res. 1975;8:165.Fristad WE, Brandvold TA, Peterson JR, Thompson SR. J Org Chem. 1985;50:3647.Snider BB, Lin H. Synth Commun. 1998;28:1913.Moriarty RM, Khosrowshahi JS. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986;27:2809.Arimoto M, Yamaguchi H, Fujita E, Nagao Y, Ochiai M. Chem Pharm Bull. 1989;37:3221.Magnus P, Lacour J. J Am Chem Soc. 1992;114:767.Chung R, Yu E, Incarvito CD, Austin DJ. Org Lett. 2004;6:3881.Sasaki T, Kanematsu K, Yukimoto Y. J Org Chem. 1972;37:890.Nocquet-Thibault S, Rayar A, Retailleau P, Cariou K, Dodd RH. Chem - Eur J. 2015;21:14205.Kamble DA, Karabal PU, Chouthaiwale PV, Sudalai A. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012;53:4195.Lu MZ, Wang CQ, Loh TP. Org Lett. 2015;17:6110.Peng H, Yuan Z, Chen P, Liu G. Chin J Chem. 2017;35:876.
-
-
-
For selected examples of electrochemical olefin diazidation methods, see: Schäfer H. Angew Chem, Int Ed Engl. 1970;9:158.Fu N, Sauer GS, Saha A, Loo A, Lin S. Science. 2017;357:575.
-
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
