Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging of Unicystic Odontogenic Tumors for Differentiation of Unicystic Ameloblastomas from Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumors
- PMID: 29354003
- PMCID: PMC5768511
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.79
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging of Unicystic Odontogenic Tumors for Differentiation of Unicystic Ameloblastomas from Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumors
Abstract
Objective: Differentiating unicystic ameloblastomas from keratocystic odontogenic tumors (KCOT) is necessary for the planning of different treatment strategies; however, it is difficult based on conventional CT and MR sequences alone. The purpose of this study was to investigate the utility of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) in the differentiation of the two tumors.
Materials and methods: We prospectively studied 40 patients with odontogenic cysts and tumors of the maxillomandibular region using conventional MR imaging and DWI. ADCs were measured using 2 b factors (500 and 1000).
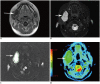
Results: Unicystic ameloblastomas (n = 11) showed free diffusion on DWI and a mean ADC value of 2.309 ± 0.17 × 10-3 mm2/s. KCOT (n = 15) showed restricted diffusion on DWI with a mean ADC value of 0.923 ± 0.20 × 10-3 mm2/s. The ADC values of unicystic ameloblastomas were significantly higher than those of KCOT (p < 0.001, Mann-Whitney U-test). An ADC cut-off value of 2.0 × 10-3 mm2/s to differentiate KCOT and unicystic ameloblastomas resulted in a 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity. Dentigerous cysts (n = 3) showed restricted diffusion on DWI and similar ADC values (1.257 ± 0.05 × 10-3 mm2/s) to those of KCOT.
Conclusion: Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC determination can be used as an adjuvant tool to differentiate between unicystic ameloblastomas and KCOT, although the ADC values of dentigerous cysts overlap with those of KCOT.
Keywords: ADC; Apparent diffusion coefficients; DWI; Diffusion-weighted MR imaging; Keratocystic odontogenic tumors; Unicystic ameloblastomas.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging in the evaluation of odontogenic cysts and tumours.Br J Radiol. 2012 Oct;85(1018):e864-70. doi: 10.1259/bjr/54433314. Epub 2012 May 2. Br J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22553294 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of ameloblastomas and keratocystic odontogenic tumors: differentiation by apparent diffusion coefficients of cystic lesions.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 Nov;29(10):1897-901. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1266. Epub 2008 Aug 21. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008. PMID: 18719033 Free PMC article.
-
Application of diffusion kurtosis imaging to odontogenic lesions: Analysis of the cystic component.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Dec;44(6):1565-1571. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25307. Epub 2016 May 17. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27185307
-
Application of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of odontogenic lesions: a systematic review.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2020 Jul;130(1):85-100.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2019.11.009. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32007494
-
Odontogenic Cysts and Neoplasms.Surg Pathol Clin. 2017 Mar;10(1):177-222. doi: 10.1016/j.path.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Dec 29. Surg Pathol Clin. 2017. PMID: 28153133 Review.
Cited by
-
Characteristics of Recent Articles Published in the Korean Journal of Radiology Based on the Citation Frequency.Korean J Radiol. 2020 Dec;21(12):1284. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.1322. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 33236548 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws: An Attempted Demonstration of the Use of Co-Word Analysis to List Main Similar Pathologies.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 9;19(4):1933. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19041933. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35206118 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional radiographic features of ameloblastoma and cystic lesions in the maxilla.Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2019 Sep;48(6):20190066. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20190066. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31124699 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of cystic lesions in the jaw by conventional magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging.Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2022 Jan 1;51(1):20210212. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20210212. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34133226 Free PMC article.
-
Florid Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia-Associated Simple Bone Cyst Showing Marked Irregular Border and High Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Value.Case Rep Dent. 2020 Sep 21;2020:8854428. doi: 10.1155/2020/8854428. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Dent. 2020. PMID: 33029434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Minami M, Kaneda T, Yamamoto H, Ozawa K, Itai Y, Ozawa M, et al. Ameloblastoma in the maxillomandibular region: MR imaging. Radiology. 1992;184:389–393. - PubMed
-
- Minami M, Kaneda T, Ozawa K, Yamamoto H, Itai Y, Ozawa M, et al. Cystic lesions of the maxillomandibular region: MR imaging distinction of odontogenic keratocysts and ameloblastomas from other cysts. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;166:943–949. - PubMed
-
- Carlson ER, Marx RE. The ameloblastoma: primary, curative surgical management. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;64:484–494. - PubMed
-
- Ecker J, Horst RT, Koslovsky D. Current role of carnoy's solution in treating keratocystic odontogenic tumors. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;74:278–282. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

